Are you struggling to choose between Agile’s flexibility and Waterfall’s structure for your next project? You’re not alone. In 2026, project managers face an increasingly complex landscape where neither pure Agile nor traditional methodologies alone can address the diverse challenges of modern project delivery. Enter hybrid project management, the strategic fusion that’s revolutionizing how organizations execute projects.
According to recent industry research, 73% of organizations expect to increase their use of hybrid project management practices over the next five years, while 89% of high-performing organizations now use hybrid approaches. This isn’t just a trend; it’s a fundamental shift in how successful projects are delivered.
This comprehensive guide explores what hybrid project management truly means in 2026, why it’s becoming the dominant methodology, and how you can implement it effectively to drive project success. You’ll discover the core principles, practical frameworks, real-world applications, and expert insights that will empower you to leverage the best of both traditional and Agile worlds.
Table of Contents:
- Section 1: Understanding Hybrid Project Management
- Section 2: Core Components of Hybrid Project Management
- Section 3: Benefits and Challenges of Hybrid Project Management
- Section 4: Implementing Hybrid Project Management in Your Organization
- Section 5: Tools and Technologies for Hybrid Project Management
- Section 6: Hybrid Project Management in Different Industries
- Section 7: Skills and Certifications for Hybrid Project Managers
- Section 8: Future Trends in Hybrid Project Management
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
Section 1: Understanding Hybrid Project Management
What Is Hybrid Project Management?
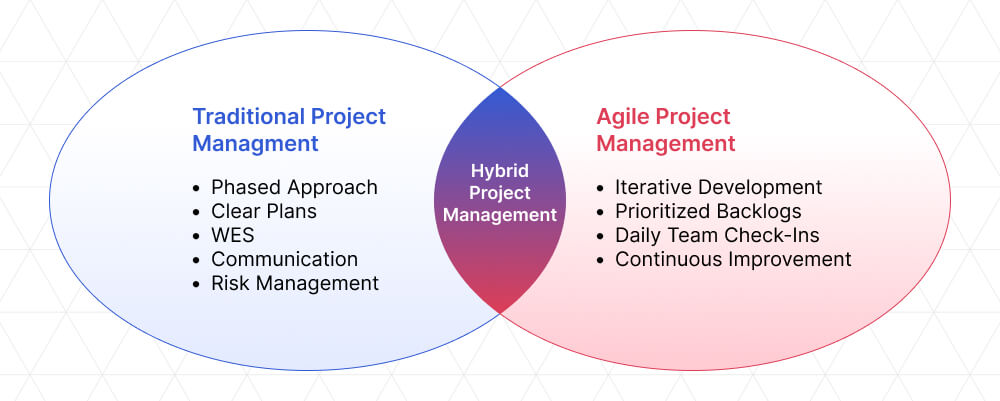
Hybrid project management is a flexible approach that strategically combines elements from both traditional (Waterfall) and Agile methodologies to create a customized framework tailored to specific project needs. Rather than rigidly adhering to a single methodology, hybrid approaches enable project managers to leverage the structured planning and documentation of Waterfall while incorporating the iterative development and adaptability of Agile.
Think of hybrid project management as a spectrum rather than a fixed formula. Some projects may lean heavily toward Waterfall with Agile elements sprinkled in, while others might adopt an Agile-first approach with traditional governance layers. The key is flexibility, choosing the right blend based on your project’s unique requirements, stakeholder expectations, and organizational constraints.
The Evolution Toward Hybrid Methodologies
The rise of hybrid project management didn’t happen overnight. It emerged from recognizing that real-world projects rarely fit neatly into a single methodology. Organizations discovered that:
- Pure Waterfall proved too rigid for projects requiring frequent changes and stakeholder feedback
- Pure Agile lacked the governance structure needed for complex, regulated, or large-scale initiatives
- Business reality demanded both predictability and flexibility simultaneously
According to the latest data, 31Companies now use hybrid models, up from just 20% in 2020. This adoption surge reflects 5% of growing organizational maturity, recognizing that methodology selection should serve project outcomes, not ideology.
Section 2: Core Components of Hybrid Project Management
The Waterfall Foundation: Structure and Governance
The traditional Waterfall methodology contributes essential structural elements to hybrid approaches. These components provide the backbone of predictability and control that stakeholders and regulatory bodies often require.
Key Waterfall Elements in Hybrid Projects:
Comprehensive Planning and Documentation: Hybrid approaches retain Waterfall’s emphasis on thorough upfront planning for major project phases. This includes detailed requirements gathering, scope definition, and architectural design that establish clear project boundaries and success criteria. Organizations that skip this critical foundation often face scope creep; 40% of projects experience scope creep in organizations lacking structured planning, compared to just 28% in well-planned projects.
Sequential Phase Gates: While not rigidly linear, hybrid methodologies incorporate phase gates at strategic points where significant decisions must be made, budgets approved, or regulatory compliance demonstrated. These gates provide stakeholders with confidence and control points without stifling innovation. For instance, a software development project might require a formal architecture approval gate before teams begin iterative development sprints.
Formalized Change Control: One of Waterfall’s most valuable contributions is structured change management. Hybrid approaches maintain formal change request processes for scope, budget, or timeline modifications that affect the project baseline. This prevents uncontrolled changes while allowing flexibility within agreed boundaries. Research shows that projects with formal change control mechanisms achieve 20% higher success rates than those without.
Predictable Budgeting and Resource Allocation: Traditional project management excels at creating detailed budgets and resource plans that span the entire project lifecycle. Hybrid methodologies leverage these capabilities to provide financial predictability while allowing tactical flexibility in how resources are deployed within approved budgets.
The Agile Advantage: Flexibility and Iteration
Agile methodologies bring adaptive capabilities that enable projects to respond to change and deliver value incrementally. These elements are crucial in today’s fast-paced business environment, where requirements evolve and early feedback drives success.
Key Agile Elements in Hybrid Projects:
Iterative Development Cycles: Instead of waiting until the end to deliver everything, hybrid approaches break work into manageable sprints or iterations, typically 2-4 weeks long. Each iteration produces deliverables for stakeholders to review and provide feedback on. This incremental approach reduces risk dramatically. Studies show that projects using iterative delivery methods achieve 27% higher success rates than big-bang approaches.
Continuous Stakeholder Engagement: Agile’s emphasis on regular collaboration transforms stakeholder engagement. Rather than formal review meetings every few months, hybrid teams conduct sprint reviews, demos, and feedback sessions every 2-4 weeks. This continuous dialogue ensures the project stays aligned with stakeholder needs and catches misunderstandings early when they’re inexpensive to fix.
Cross-Functional Team Collaboration: Agile’s self-organizing, cross-functional teams bring together diverse expertise to solve problems collaboratively. In hybrid projects, these teams operate within the boundaries established by traditional planning but have autonomy in how they achieve sprint goals. This balance between empowerment and structure creates highly engaged teams that take ownership of outcomes.
Adaptive Planning and Reprioritization: While the overall project roadmap remains stable, hybrid approaches enable tactical adjustments based on learning and evolving priorities. Product backlogs are regularly refined, and sprint planning sessions adapt to new insights. This flexibility is essential; 58% of financial services companies now use Agile methods regularly, precisely because they need to respond rapidly to market changes and regulatory shifts.
The Integration Challenge: Making Hybrid Work
Successfully combining Waterfall and Agile elements requires thoughtful integration rather than simply mixing techniques randomly. Organizations that excel at hybrid project management follow these integration principles:
Clear Boundary Definition: Successful hybrid teams explicitly define which aspects of the project follow traditional approaches and which use Agile methods. For example, a construction project might use Waterfall for structural engineering and permitting while employing Agile for interior design selections and client customizations.
Governance Frameworks That Enable Both: Hybrid projects need governance structures that provide oversight without micromanagement. This often means phase gates for major decisions combined with delegated authority for sprint-level choices. PMI research indicates that organizations with mature governance models see project success rates 57% higher than those with poorly defined governance.
Unified Reporting and Metrics: One of the biggest challenges in hybrid projects is creating reporting that satisfies both traditional and Agile stakeholders. Successful hybrid approaches develop dashboards that show both phase completion (Waterfall) and velocity/burndown charts (Agile), giving everyone the view they need.
| PRO TIP:
Start small when transitioning to hybrid methodologies Choose a pilot project with manageable complexity and supportive stakeholders. Document what works and what doesn’t, then scale successful practices across the organization. This iterative approach to methodology adoption significantly increases success rates and team buy-in. |
Section 3: Benefits and Challenges of Hybrid Project Management
Strategic Benefits: Why Organizations Choose Hybrid
The surge in hybrid adoption isn’t accidental; organizations are seeing tangible benefits that directly impact project success rates and business outcomes.
Enhanced Flexibility Without Chaos: Hybrid approaches provide the perfect balance organizations crave. Teams can respond to changing requirements and market conditions while maintaining the structure needed for predictable delivery. This flexibility is particularly valuable in digital transformation initiatives, where 90% of organizations are undergoing some type of digital transformation and need methodologies that can adapt as technology and requirements evolve.
Improved Stakeholder Satisfaction: By combining comprehensive upfront planning with regular incremental deliveries, hybrid methodologies meet diverse stakeholder preferences. Executive sponsors appreciate the predictability of phase gates and budget controls, while end users value frequent opportunities to see and influence the evolving solution. Research shows that projects with continuous stakeholder engagement achieve 25% higher satisfaction scores than those with limited stakeholder touchpoints.
Risk Mitigation Through Early Validation: One of hybrid methodology’s most powerful advantages is its ability to validate assumptions early through Agile iterations while maintaining risk management frameworks used in traditional approaches. Teams can test critical assumptions in sprints 1-2 rather than discovering problems in the final testing months. Organizations using this approach report up to 30% reduction in project failures due to requirements misunderstandings.
Optimized Resource Utilization: Hybrid methodologies enable more efficient resource allocation by combining long-term resource planning (Waterfall) with flexible sprint-based deployment (Agile). Project managers can plan for major resource needs months in advance while maintaining the flexibility to adjust team composition sprint by sprint based on actual progress and priorities. This optimization is critical, strategic resource allocation can minimize idle time by up to 25% and maximize productivity across project portfolios.
Regulatory Compliance With Innovation: Many industries face strict regulatory requirements that seem incompatible with Agile’s flexibility. Hybrid approaches solve this by using Waterfall’s structured documentation and approval processes for compliance-critical elements while enabling Agile innovation in non-regulated areas. 76% of construction companies rely on predictive project management for exactly this reason, regulatory compliance and safety requirements demand structure, but they’re increasingly incorporating hybrid elements for design and client interaction phases.
Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
While hybrid methodologies offer significant advantages, they also present unique challenges that organizations must address proactively.
Methodology Confusion and Inconsistency: One of the most common pitfalls occurs when teams aren’t clear about which methodology applies to which project elements. This confusion leads to inconsistent practices, frustrated team members, and stakeholder dissatisfaction. The solution lies in creating explicit methodology maps that clearly define which approaches apply to different project phases, deliverables, or workstreams.
Tool and Process Integration Complexity: Traditional project management and Agile teams often use different tools, Gantt charts versus Kanban boards, for example. Integrating these tools and processes creates technical and cultural challenges. Modern project management platforms, such as those that support hybrid methodologies, help by providing unified views that accommodate both perspectives. Organizations investing in proper tooling see 20% improvements in team collaboration and reporting efficiency.
Team Member Skill Gaps: Hybrid project management requires team members to be fluent in both traditional and Agile concepts. However, only 45% of organizations provide accredited project management training, leaving many team members struggling to understand when and how to apply different techniques. Addressing this requires comprehensive training programs that go beyond basic certification to include hands-on experience with hybrid approaches.
Balancing Documentation and Agility: Finding the right level of documentation is a perpetual challenge in hybrid projects. Too much documentation slows agility; too little creates compliance and knowledge transfer risks. Successful hybrid teams establish clear documentation standards that specify what must be documented formally (e.g., architecture decisions, regulatory compliance, major design choices) versus what can remain lightweight (e.g., sprint planning notes, daily stand-up outcomes).
| AVOID THIS MISTAKE
Don’t implement hybrid project management without adequate training and change management. Many organizations assume teams can naturally blend methodologies, leading to confusion and resistance. Why it’s problematic: Untrained teams often revert to familiar approaches under pressure, losing hybrid methodology benefits and creating inconsistent practices that frustrate stakeholders. What to do instead: Invest in comprehensive training programs, establish clear methodology guidelines, and provide coaching support during the transition period. Organizations that prioritize change management see 27% higher adoption rates and significantly better outcomes. |
Section 4: Implementing Hybrid Project Management in Your Organization
Assessment: Is Hybrid Right for Your Projects?
Before diving into hybrid project management, organizations should carefully assess whether this approach aligns with their project characteristics, organizational culture, and strategic objectives.
Project Characteristics That Favour Hybrid Approaches: Certain project types particularly benefit from hybrid methodologies. These include projects with well-defined end goals but evolving requirements, initiatives requiring regulatory compliance alongside innovation, large-scale transformations with multiple workstreams, and projects where stakeholder involvement is critical but must be balanced with predictable timelines.
Consider a financial services company implementing a new customer portal. The overall architecture, security requirements, and regulatory compliance components demand Waterfall’s structure and documentation. However, user interface design, feature prioritization, and user experience optimization benefit enormously from Agile’s iterative approach and frequent user feedback. This scenario is ideal for hybrid methodology.
Organizational Readiness Factors: Beyond project characteristics, organizational factors significantly influence hybrid project success. Organizations with mature project management practices, supportive leadership willing to invest in training and tools, cross-functional collaboration capabilities, and tolerance for methodological experimentation tend to succeed with hybrid approaches. Conversely, organizations with rigid cultures, siloed departments, or resistance to change may struggle initially and need focused change management efforts.
Framework Selection and Customization
Multiple hybrid frameworks exist, each with different emphases and applications. Selecting and customizing the right framework for your organization is crucial.
Popular Hybrid Frameworks in 2026:
Water-Scrum-Fall: This approach uses Waterfall for initiation and planning, Scrum for execution and development, and returns to Waterfall for final testing and deployment. It’s particularly effective for software development projects within traditionally-managed organizations.
Agile-Stage-Gate: Originally developed for product development, this framework applies Agile methods within traditional stage-gate structures. Each stage gate represents a major decision point, but work within stages follows Agile principles. This framework works exceptionally well for innovation projects requiring executive oversight and funding approval at specific milestones.
PRINCE2 Agile: This formalized approach combines PRINCE2’s governance framework with Agile delivery, providing structured project management roles and processes while enabling Agile execution. PRINCE2 Agile will see increased adoption in 2026 as organizations seek methods that balance governance with responsiveness, particularly in regulated industries.
Disciplined Agile Delivery (DAD): DAD provides a comprehensive toolkit for hybrid delivery, offering guidance on when and how to apply different techniques based on project context. It’s particularly valuable for organizations managing diverse project portfolios requiring different methodological blends.
Step-by-Step Implementation Roadmap
Successfully implementing hybrid project management requires a structured, phased approach rather than overnight transformation.
Phase 1: Foundation Building (Months 1-2): Begin by establishing clear objectives for hybrid adoption and assessing current project management maturity. Create a hybrid methodology working group including representatives from traditional PM, Agile, and business stakeholder communities. This group will define your organization’s hybrid approach, including which elements from each methodology to retain, how they’ll integrate, and what governance structure will oversee hybrid projects.
During this phase, select pilot projects carefully. Choose initiatives with moderate complexity, supportive stakeholders, and team members open to experimentation. Avoid starting with your most critical or politically sensitive projects, save those for after you’ve refined your approach through pilot experience.
Phase 2: Pilot Execution (Months 3-6): Launch pilot projects using your defined hybrid framework, providing intensive coaching and support. Conduct regular retrospectives not just on project progress but on the methodology itself, what’s working, what’s creating friction, and what needs adjustment. Document lessons learned in real-time rather than waiting until project completion.
Create visible success stories from pilot projects. Share accomplishments, metrics improvements, and stakeholder testimonials widely across the organization. This builds momentum and reduces resistance from teams wondering if they’ll be required to adopt hybrid approaches next.
Phase 3: Refinement and Scaling (Months 7-12): Based on pilot learnings, refine your hybrid framework and supporting processes. Develop comprehensive training programs for project managers, team members, and stakeholders. Update templates, tools, and governance structures to support hybrid delivery.
Begin scaling to additional projects, prioritizing those most likely to benefit from hybrid approaches. Continue intensive support for newly-hybrid projects while gradually reducing support for mature hybrid teams. Establish communities of practice where hybrid practitioners share experiences, challenges, and solutions.
Phase 4: Organizational Integration (Months 13+): Integrate hybrid project management into organizational standards and career paths. Update project management competency models to include hybrid skills. Refine PMO processes to support diverse methodological approaches. Continuously evolve your hybrid framework based on ongoing experience and emerging best practices.
Section 5: Tools and Technologies for Hybrid Project Management
Essential Software Capabilities
Modern project management software has evolved to support hybrid methodologies, offering features that accommodate both traditional and Agile approaches within a single platform.
Unified Project Views: Leading platforms offer customizable dashboards that display Gantt charts for executives who prefer traditional views, alongside Kanban boards and burndown charts for Agile teams. This flexibility ensures all stakeholders can access information in formats that make sense to them.
Flexible Planning Tools: Hybrid project management software supports both long-term roadmap planning and short-term sprint planning. Teams can establish major milestones and phase gates (Waterfall) while maintaining product backlogs and conducting sprint planning sessions (Agile) within the same tool.
Automated Reporting and Metrics: Advanced platforms automatically generate reports combining traditional metrics (schedule variance, budget performance) with Agile metrics (velocity, sprint burndown, team capacity). This eliminates the manual overhead of maintaining separate reporting systems.
Resource Management Across Methodologies: Sophisticated resource management capabilities enable organizations to plan long-term resource needs while allowing flexible, sprint-based allocation. This is particularly valuable for organizations managing multiple concurrent projects with shared resource pools.
Popular Tools for Hybrid Delivery in 2026
Several project management platforms have emerged as leaders in supporting hybrid methodologies:
Enterprise-grade solutions such as Wrike, Monday.com, and Smartsheet offer comprehensive hybrid capabilities, including advanced reporting, enterprise governance features, extensive integrations, and support for both traditional and Agile workflows. These platforms typically serve mid-sized to large organizations managing complex project portfolios.
Agile-native platforms with Traditional Extensions, such as Jira and Azure DevOps, originally focused on Agile but now include roadmap planning, traditional reporting, and governance features that support hybrid approaches. These work particularly well for technology-focused organizations transitioning from pure Agile to a hybrid approach.
Traditional PM Tools with Agile Capabilities like MS Project and Primavera have added Agile features to their traditional project management foundations, supporting organizations with deeply embedded traditional practices that want to incorporate Agile elements gradually.
The key is to select tools that genuinely integrate both methodologies rather than bolt on superficial features. Look for platforms where Agile and traditional elements share the same underlying data model, ensuring consistency and eliminating duplicate data entry.
| PRO TIP
Don’t let tool selection drive your methodology—let methodology needs drive tool selection. Many organizations choose tools first, then force their processes to fit tool constraints. Instead, define your hybrid approach clearly, then select tools that support your chosen methodology blend. This ensures tools enable your success rather than constrain your options. |
Section 6: Hybrid Project Management in Different Industries
Technology and Software Development
The technology sector has been at the forefront of hybrid adoption, recognizing that pure Agile doesn’t always accommodate enterprise architecture requirements and governance needs.
Typical Hybrid Approach: Technology companies often use Waterfall for initial architecture design, security planning, and compliance assessment, then shift to Agile sprints for feature development and testing. Final deployment and cutover may return to structured Waterfall-style release management.
Financial Services and Banking
Financial institutions face unique challenges balancing regulatory compliance with the need for rapid digital innovation. 58% of financial services companies now use Agile methods regularly, but almost always in hybrid configurations.
Typical Hybrid Approach: Banks employ Waterfall for regulatory-mandated documentation, audit trails, and governance while using Agile for customer-facing digital features and internal process improvements. Phase gates ensure compliance checkpoints while sprints enable rapid feature delivery.
Construction and Engineering
Construction projects exemplify why hybrid approaches matter. 76% of construction companies still rely heavily on predictive project management due to permitting, safety regulations, and sequential physical work requirements. However, they’re increasingly incorporating Agile elements.
Typical Hybrid Approach: Construction projects use Waterfall for design, permitting, structural work, and safety planning, while employing Agile for interior finishing, client customizations, and technology integrations. This approach leverages flexibility to add value without compromising structural integrity.
Healthcare and Pharmaceuticals
Healthcare organizations balance rigid FDA and regulatory requirements with the need for innovation and patient-centric design, making hybrid approaches particularly relevant.
Typical Hybrid Approach: Healthcare projects use Waterfall for regulatory compliance documentation, clinical validation, and safety protocols while employing Agile for user interface design, workflow optimization, and system integration where iterative refinement improves outcomes.
Section 7: Skills and Certifications for Hybrid Project Managers
Essential Competencies
Hybrid project managers require a unique blend of technical and interpersonal capabilities spanning both traditional and Agile domains.
Traditional Project Management Skills remain foundational, including scope management, schedule development, budget planning, risk management, and stakeholder communication. These competencies ensure project managers can establish the structure and predictability that hybrid projects require.
Agile and Adaptive Skills are equally critical, encompassing sprint planning, backlog management, facilitating Agile ceremonies, and fostering self-organizing teams. Project managers must be comfortable with ambiguity and changing requirements.
Integration and Judgment Capabilities represent the meta-skill that distinguishes truly effective hybrid project managers: knowing when to apply which methodology, how to blend techniques effectively, and how to navigate conflicts between Agile and traditional stakeholders.
Relevant Certifications for 2026
Professional certifications validate hybrid project management expertise and open career opportunities. 33% of professionals with PMP certification report higher median salaries than those without certification.
PMP (Project Management Professional): The gold-standard certification from PMI now explicitly covers hybrid approaches alongside predictive and Agile methodologies. The PMP certification proves you have project leadership and expertise in any way of working: predictive, hybrid, or agile.
PRINCE2 Agile: This certification specifically addresses hybrid delivery by combining PRINCE2’s governance framework with Agile execution practices. It’s particularly valuable for project managers working in European or government contexts.
PMI-ACP (Agile Certified Practitioner): While focused on Agile, this certification provides deep knowledge of adaptive approaches that complement traditional PM certifications in hybrid contexts.
SAFe Certifications: For organizations implementing Scaled Agile Framework, SAFe certifications demonstrate expertise in scaling Agile practices across large enterprises, a fundamentally hybrid challenge.
Section 8: Future Trends in Hybrid Project Management
AI and Automation in Hybrid Projects
Artificial intelligence is transforming hybrid project management by automating routine tasks and providing data-driven insights that enhance decision-making. 82% of senior leaders say AI will have at least some impact on how projects are run over the next five years.
AI-powered tools now assist with intelligent scheduling recommendations, risk prediction and mitigation suggestions, automated progress tracking and reporting, and resource optimization across methodologies. These capabilities allow project managers to focus on strategic decisions rather than administrative overhead.
Increased Focus on Value Delivery
The future of hybrid project management emphasizes outcomes over outputs. Rather than simply delivering on time and on budget, organizations increasingly measure projects by business value generated, benefits realization, and strategic alignment. This shift requires hybrid methodologies to incorporate value-based prioritization and continuous benefits tracking.
Sustainability and ESG Integration
48% of organizations identify Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) projects as top priorities for their technology teams in the coming years. Hybrid project management must evolve to incorporate sustainability metrics, ethical considerations, and social impact assessment alongside traditional success criteria.
Conclusion
Hybrid project management has emerged as the intelligent response to the complex, dynamic project landscape of 2026. By strategically combining Waterfall’s structure and governance with Agile’s flexibility and responsiveness, hybrid methodologies enable organizations to deliver successful projects in environments where neither pure approach would suffice alone.
The statistics speak clearly: organizations adopting hybrid approaches see 20% higher success rates, improved stakeholder satisfaction, and better ability to navigate change and uncertainty. As 73% of organizations plan to increase their use of hybrid methodologies over the next five years, project managers who master these approaches position themselves at the forefront of their profession.
Whether you’re managing technology implementations, construction projects, financial services initiatives, or any complex undertaking, hybrid project management provides the framework to balance competing demands for structure and flexibility, predictability and adaptability, governance and innovation.
Your journey toward hybrid project management expertise begins with understanding these principles, experimenting thoughtfully with blended approaches, investing in professional development, and committing to continuous learning as methodologies evolve. The future belongs to project managers who can navigate complexity with confidence, applying the right methodological blend to each unique project challenge.
Take the next step in your project management career by exploring professional certification programs that validate your hybrid project management expertise. The project management landscape is evolving; ensure you’re equipped with the skills, knowledge, and credentials to lead successful projects in 2026 and beyond.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What exactly is hybrid project management?
Hybrid project management is a flexible approach that combines elements from both traditional (Waterfall) and Agile methodologies, allowing project managers to leverage structured planning and documentation alongside iterative development and adaptability. It creates customized frameworks tailored to specific project needs rather than rigidly adhering to a single methodology.
2. How do I know if my project needs a hybrid approach?
Projects with well-defined end goals but evolving requirements, those requiring regulatory compliance alongside innovation, large-scale transformations with multiple workstreams, and initiatives where stakeholder involvement is critical but must be balanced with predictable timelines are ideal candidates for hybrid methodologies.
3. What are the main challenges in implementing hybrid project management?
Common challenges include confusion and inconsistency in methodology, complexity of tool and process integration, skill gaps among team members, and balancing documentation needs with agility. These challenges can be overcome through clear methodology mapping, comprehensive training, appropriate tooling, and strong change management.
4. Which industries benefit most from hybrid project management?
While hybrid approaches work across industries, they’re particularly valuable in financial services (58% of firms use Agile regularly), technology companies that balance enterprise architecture with innovation, healthcare organizations navigating regulatory requirements, and construction firms that incorporate flexibility into traditionally structured projects.
5. What certifications are most valuable for hybrid project managers?
The PMP® (Project Management Professional) certification is the gold standard and now explicitly covers hybrid approaches. PRINCE2 Agile specifically addresses hybrid delivery, while PMI-ACP validates Agile expertise. Many successful hybrid project managers hold multiple certifications spanning traditional and Agile domains.
6. How long does it take to implement hybrid project management organization-wide?
A phased implementation typically takes 12-18 months, starting with foundation building and pilot projects (months 1-6), followed by refinement and scaling (months 7-12), and finally organizational integration (months 13+). However, pilot projects can show results within 3-6 months.
7. What tools are best for managing hybrid projects in 2026?
Leading platforms include Wrike, Monday.com, Smartsheet, Jira, and Azure DevOps, each offering unified views that accommodate both Gantt charts and Kanban boards, flexible planning tools, automated reporting combining traditional and Agile metrics, and resource management across methodologies. Tool selection should align with your specific hybrid approach rather than driving it.