In 2026, cloud computing remains the invisible engine behind nearly every digital experience we rely on, from streaming platforms and AI tools to remote work systems and smart devices. It has reshaped how individuals, startups, and global enterprises store data, run applications, and scale innovation.
But what makes cloud computing so transformative? Why have most organizations moved their operations to “the cloud,” and what exactly happens behind the scenes when they do?
This guide breaks it down – exploring how cloud computing works, its main types, real-world examples, key benefits, and why it continues to drive business growth worldwide.
Before moving forward, let’s discuss the cloud computing definition
What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud Computing is the concept of providing various services over the internet. It transforms the computing infrastructure into a simpler, more accessible form. Moreover, we can easily access and store applications remotely and move everything to cloud-based services. The base of cloud computing is the Internet. If you have internet access, you can access all your needs remotely.
| “Cloud computing is a huge enabler of innovation. It’s where you can experiment, scale fast, and bring new ideas to market.” |
Cloud Computing is mainly based on the physical Information Technology resources available. The basic concept is to locate all the infrastructure at different locations and access it easily, at any time. Many organizations are moving to cloud computing, recognizing its advantages. In conclusion, it reduces the cost of purchasing individual computing components.
Cloud computing is a method of accessing data centers, servers, storage, computing power, databases, and networking components. It’s a capsule containing all the infrastructure components. You can access them as needed. In addition, there are many cloud service providers in the market, and you have to choose based on your needs and budget. Above all, Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud Platform, and Microsoft Azure are the top performers in the market, with extensive experience and feature sets.
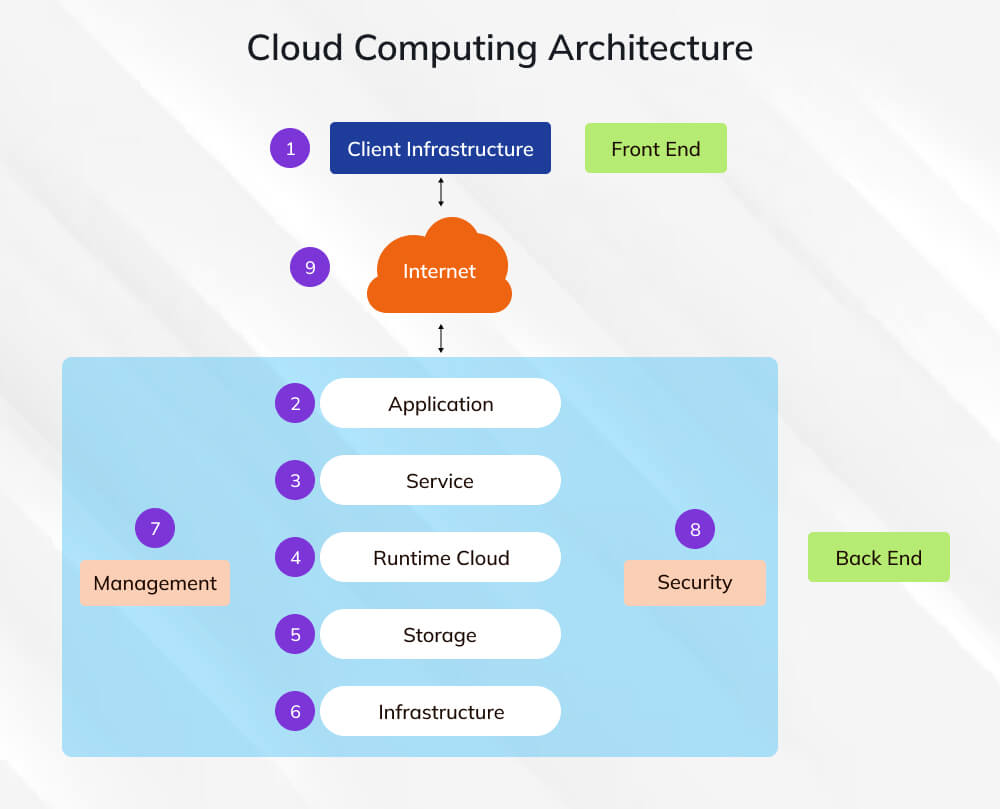
How Does Cloud Computing Work?
To understand how cloud computing works, imagine two sides of a system: the front end (what you see and use) and the back end (where all the heavy computing occurs). These two are connected through the internet, which acts as the bridge between your device and the cloud.
On the front end, users interact with web applications, browsers, or mobile apps to send requests, for example, opening a file in Google Drive or streaming a show on Netflix.
On the back end, vast data centers operated by cloud providers handle those requests. They include servers, databases, storage systems, and application software that process data and deliver results back to users, instantly and securely.
Cloud computing enables you to utilize computing power and storage resources located elsewhere, rather than relying on your own hardware.
This design ensures scalability, reliability, and cost efficiency, the core reasons why nearly every modern service today runs in the cloud.
Types of Cloud Computing Services
Cloud computing services are typically categorized into three main categories:
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS).
- Each offers a different level of control, flexibility, and user management.
Together, these models form the foundation for delivering computing resources over the internet.
1. Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
IaaS provides virtualized computing infrastructure over the internet, including servers, networks, and storage, on a pay-as-you-go basis.
It provides organizations with complete control over their IT resources, eliminating the need for investment in physical hardware.
Examples
Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud, DigitalOcean.
Best For
Developers and businesses need scalable resources to build or host applications from scratch.
Key Benefits
- Full control over servers and configurations.
- Highly scalable and cost-efficient.
- Ideal for startups and enterprises alike.
2. Platform as a Service (PaaS)
PaaS provides a ready-to-use development and deployment environment for building, testing, and managing applications, without requiring the management of underlying hardware or operating systems.
Examples
Google App Engine, Heroku, Microsoft Azure App Service.
Best For
Developers who want to focus on coding rather than infrastructure setup or maintenance.
Key Benefits
- Simplifies app development and testing.
- Reduces time to market.
- Automatically manages scalability and updates.
3. Software as a Service (SaaS)
SaaS delivers fully functional software applications over the internet.
Users access these tools via a web browser, eliminating the need for installation or maintenance.
Examples
Salesforce, Slack, Zoom, Google Workspace, Dropbox.
Best For
Businesses and individuals need easy-to-use software that is accessible from any device.
Key Benefits
- No installation or maintenance costs.
- Accessible from anywhere.
- Subscription-based pricing with instant updates.
Comparison: IaaS vs PaaS vs SaaS
| Feature | IaaS | PaaS | SaaS |
| User Control | Full control over infrastructure | Control over applications and data | Limited control (only user settings) |
| Main Purpose | Build and host IT infrastructure | Develop and deploy applications | Use software applications online |
| Target Users | IT admins, developers | Developers | End users, teams, businesses |
| Examples | AWS, Azure, Google Cloud | Heroku, Google App Engine | Slack, Salesforce, Zoom |
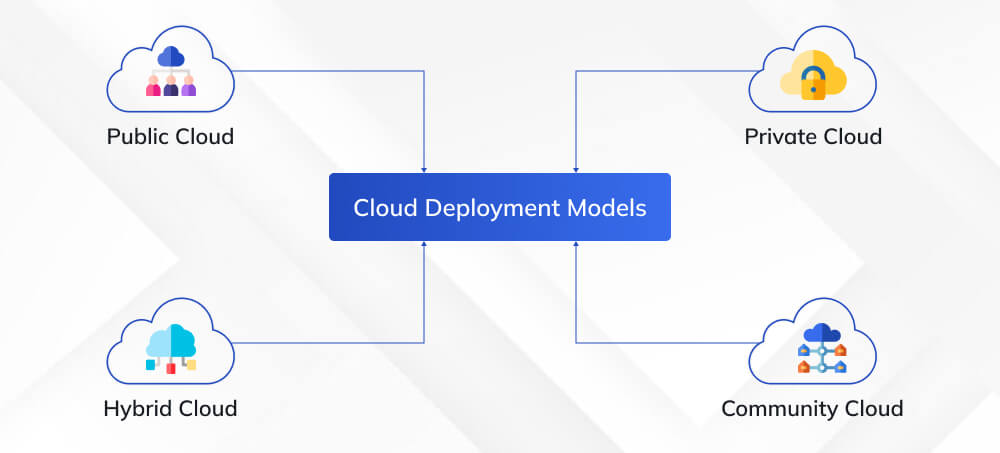
Cloud Computing Deployment Models
The cloud deployment model identifies the type of cloud environment based on ownership, scale, access, and the nature and purpose of the cloud. Furthermore, different deployment models are used depending on the location and who manages the infrastructure.
To make the best use of a specific cloud deployment type, you must first understand what each deployment model can do, its characteristics, and its advantages and disadvantages.
Public Cloud
The public cloud, as the name implies, is open to the general public, and resources are shared among all users. Anyone, anywhere, can access them via the internet. One of the most common cloud deployment models is the public cloud. Alibaba Cloud, Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud, IBM Cloud, and Microsoft Azure are among the largest public cloud providers.
The vendor’s data center hosts this computing model. The public cloud model makes resources like storage and applications available to the general public via the internet. Furthermore, it fulfills all requests; resources are nearly limitless.
Characteristics of Public Cloud
The following are the essential characteristics of the Public Cloud:
- Uniformly designed Infrastructure.
- Scale economies.
- SLA ensures that all users have a fair share with no priority.
- Operates on a Pay-as-you-go basis.
- It is a multi-tenant architecture; therefore, data is highly likely to be leaked.
Advantages of Public Cloud
- Simple to use: The great thing about a managed service is that there is very little maintenance for you and your team. The setup is handled, and there is no need for you to develop your tools, as this is also handled.
- Cost: Because services are billed this way, you do not pay for items you do not use. As a result, you can pay more when you need more resources and then reduce your payments when things return to normal.
- Performance and dependability: Most businesses’ primary concern is uptime. When your systems fail, your business suffers. Many of these cloud service providers provide excellent uptime and service availability.
Disadvantages of Public Cloud
- There is less control: You must have command over the systems that host your business applications. If a public cloud platform fails, you do not have access to ensure continuity, as you would in a traditional server room or data center environment.
- Security and privacy: Segmentation must be carried out to the highest standard to ensure no cross-contamination between clients using the same hardware on a public cloud.
- Simple environments: Most businesses have specific needs for customized services. Many cloud platforms offer only basic functionality, with few customization options.
Private Cloud
The private cloud deployment model is a dedicated environment for a single user or customer. You do not share any hardware with other users because it is all yours.
Sharing your hardware is not necessary because it is a one-to-one environment for single use. The primary distinction between private and public cloud deployment models is how the hardware is handled. It’s also known as the “internal cloud,” referring to the ability to access systems and services within a company or across borders.
Characteristics of Private Cloud
Here are the essential characteristics of the Private Cloud:
- It has a non-uniformly designed infrastructure.
- Extremely low risk of data leaks.
- Internal Infrastructure to manage resources easily.
- Offers End-to-End Control.
- SLA is poor, but you can implement custom policies.
Advantages of Private Cloud
- Increased Control: You are the property’s sole owner. As a result, you gain complete control over service integration, information technology operations, policies, and user behavior.
- Legacy System Support: This method is intended for legacy systems that cannot connect to the public cloud.
- Customization: A private cloud deployment, as opposed to a public cloud deployment, allows a company to tailor its solution to meet its specific needs.
- Data Protection and Privacy: It is appropriate for storing corporate information that only authorized personnel can access. However, improved access and security can be achieved by segmenting resources within the same infrastructure.
Disadvantages of Private Cloud
- Scalability is reduced: With fewer clients, private clouds can be scaled only within a certain range.
- Expensive: Private clouds are more expensive because they provide personalized services.
Hybrid Cloud
Public and private clouds are combined in a hybrid cloud deployment model. A hybrid cloud computing model is one in which a company uses the public cloud while owning on-premises systems and connecting the two. As a result, they operate as a single system, an advantageous model for a gradual transition to the public cloud.
Because of security concerns or data protection requirements, some businesses cannot operate solely in the public cloud. As a result, they may opt for a hybrid cloud to meet their needs while also reaping the benefits of a public cloud. For example, it allows on-premises applications containing sensitive data to coexist with public cloud applications.
Characteristics of Hybrid Cloud
Here are the Characteristics of the Hybrid Cloud:
- Cost-effective Cloud Deployment Model.
- Offers better security and privacy.
- Makes data and application portability easier.
- Provides increased scalability.
Advantages of Hybrid Cloud
- Flexibility: One of the best aspects of this cloud type is its adaptability. You can integrate the best features of each cloud type into your solution.
- Scalability: Any platform’s limitations do not bind you. This means you can scale up or down in response to user demand.
Disadvantages of Hybrid Cloud
- Cost: When using a hybrid cloud, you may overspend. Compared with other types of clouds, hybrid clouds are relatively inexpensive. However, there is a risk of overspending if you are not careful in selecting the right services.
- Data silos. If you use public and private services, you must ensure that your data is properly separated. This can increase your company’s security, compliance, and auditing requirements.
Community Cloud
Community clouds are cloud-based infrastructure models that allow multiple organizations to share resources and services in accordance with regulatory standards. It provides organizations with a shared platform and resources to work on their business requirements. This Cloud Computing model is run and managed by community members, third-party vendors, or both. Members of the community cloud are organizations that share common business requirements.
Advantages of Community Cloud
- Cost reduction.
- Enhanced security, privacy, and reliability.
- Ease of data sharing and collaboration.
Disadvantages of Community Cloud
- Very expensive compared to the public deployment model.
- Sharing of fixed storage and bandwidth capacity.
- Customization in rigid.
Major Benefits of Cloud Computing
In 2026, cloud computing is no longer just an IT choice; it’s a business growth strategy.
From startups to global enterprises, organizations rely on the cloud to move faster, reduce costs, and stay resilient in a rapidly changing market.
| According to Gartner’s report, global spending on public cloud services is expected to reach USD 679 billion, a 20.4% increase from the previous year, demonstrating the critical importance of the cloud to modern business operations. |
Here are the major benefits of cloud computing that drive this massive adoption:
1. Cost Efficiency
Cloud computing eliminates the need for large upfront investments in hardware and maintenance. You only pay for what you use, making it ideal for both startups and enterprises managing fluctuating workloads.
Example: Netflix reduced infrastructure costs by migrating its entire infrastructure to AWS.
2. Scalability and Flexibility
Businesses can scale their infrastructure up or down within minutes. Whether it’s a seasonal traffic spike or a new product launch, cloud resources adjust instantly without disrupting operations.
3. Business Continuity and Reliability
Cloud platforms offer built-in backup, failover, and disaster recovery capabilities. This ensures that data and applications remain available, even during outages or cyber incidents.
4. Improved Collaboration and Accessibility
Since cloud services are internet-based, teams can access files, applications, and tools from anywhere, enabling remote work. This enables remote work, real-time collaboration, and productivity across global locations.
5. Enhanced Security
Leading cloud providers, such as AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud, invest billions of dollars annually in cybersecurity. They offer multi-layered protection, including encryption, identity management, and continuous monitoring, often exceeding what most organizations can manage internally.
6. Faster Innovation
Cloud computing allows companies to experiment and deploy new solutions without delay. With low entry barriers and scalable resources, innovation becomes faster and more cost-effective.
7. Stainability and Energy Efficiency
Cloud providers are increasingly investing in renewable energy-powered data centers, reducing the carbon footprint of IT operations. By consolidating workloads in optimized environments, the cloud supports global sustainability goals.
Conclusion
Cloud computing has evolved beyond being just a technology; it has become the core infrastructure driving digital innovation across various industries. From startups to global enterprises, every organization is embracing the cloud to operate more efficiently, quickly, and securely.
As businesses evolve toward hybrid and multi-cloud ecosystems, the need for professionals who can design, secure, and optimize cloud environments continues to grow. For learners and working professionals, this presents a tremendous opportunity to build future-ready skills and stay competitive in a cloud-first economy.
At Invensis Learning, we empower individuals and teams to develop those capabilities through comprehensive Certification Training programs. Designed by industry experts, our courses help you understand service models, deployment strategies, and real-world applications, enabling you to apply cloud concepts confidently in your role.