Projects drive growth, innovation, and success. Ensuring these projects are managed effectively is crucial for an organization’s overall success and sustainability. But how does one guarantee that every project, big or small, is completed on time, within scope, and under budget? The answer lies in leveraging the right project management techniques and tools.
Every project, regardless of its domain or industry, has unique challenges. However, certain time-tested tools and techniques have been developed that can be universally applied to optimize project management.
This blog will delve deep into the 10 most important project management techniques. While the tools provide the tangible means to plan, schedule, and monitor progress, the techniques are the strategies that make the application of these tools seamless and result-driven.
Table of Contents:
What are Project Management Techniques?
Project Management Techniques refer to specific methods, processes, and approaches project managers and teams employ to initiate, plan, execute, monitor, and close projects. These techniques are the blueprints that guide project professionals in breaking down complex tasks into manageable units, setting milestones, allocating resources efficiently, managing risks, and ensuring timely completion.
In essence, these techniques are the strategic framework that ensures a project’s journey from conception to completion is smooth and systematic. They provide a structured pathway and tools to measure progress, identify bottlenecks, and ensure alignment with the project’s objectives and stakeholders’ expectations.
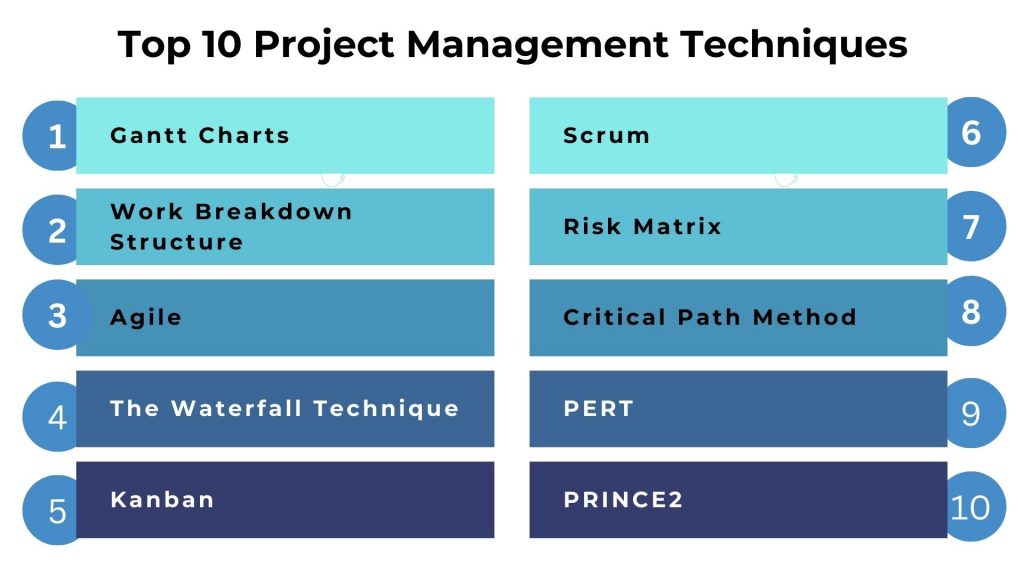
Top 10 Project Management Techniques
Delve into the ten most impactful project management techniques that guide you and your teams to achieve goals efficiently. These strategies, rooted in proven practices, provide a roadmap for project initiation, execution, and successful closure.
-
Gantt Charts
Gantt charts dissect extensive project processes into more digestible segments, allowing teams to navigate and execute efficiently.
Using the analogy of plotting a journey, consider Gantt charts as your roadmap. The journey may involve setting the route, scheduling breaks, and monitoring travel progress.
Why opt for Gantt charts?
Primarily a navigation aid in project journeys, Gantt charts are versatile instruments adaptable to various project methodologies. They guarantee a comprehensive view of all milestones and resources necessary to reach the destination.
Embarking on a Gantt chart journey?
Begin with the end goal in mind, then chart out the landmarks and steps needed to get there. Partition these milestones into more specific segments, halting only when further subdivision isn’t feasible.
-
Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)
A Work Breakdown Structure deconstructs major project activities into smaller, more manageable tasks that teams can comprehend and execute.
Taking the example of building a house, you might categorize the work into areas like interior tasks, exterior tasks, and laying the foundation.
These segments are then subdivided into more specific work packages, considering hierarchy and task interdependencies.
Who is WBS for?
While primarily a project management method, WBS doubles as a tool that can complement various techniques. It provides clarity on all tasks and resources needed for the final product.
How to begin?
Kick-off by focusing on the project’s final output and then outlining the tasks essential for its completion by you and your team.
Segment these tasks into defined work packages. Continue this process until you’re confident the tasks can’t be divided further.
-
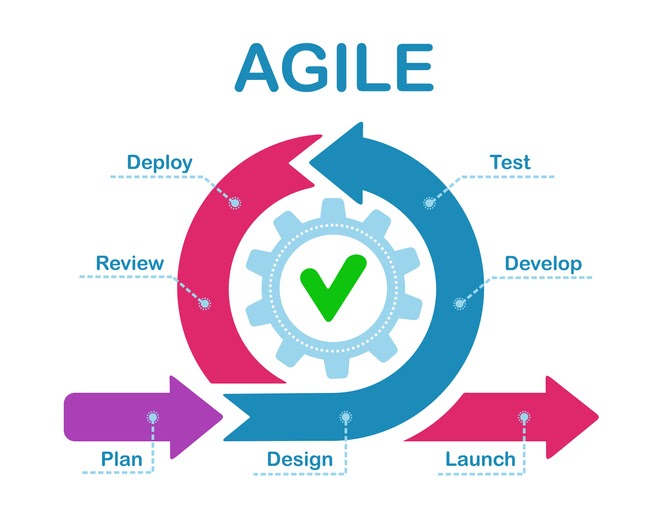
Agile
The Agile approach breaks down projects into short-term goals that result in quickly achievable deliverables. It’s an ideal strategy for projects demanding swift action and adaptability. By adopting the Agile methodology, teams are empowered to manage their tasks autonomously, make informed decisions in line with the collective objective, and swiftly realign their priorities when needed.
Who is it for?
Agile suits teams and organizations that value adaptability, stakeholder feedback, and iterative progress. It’s especially beneficial for projects with evolving requirements or where the end goal is flexible.
How to begin?
Kick-starting Agile involves understanding its core principles and values. Begin by assembling a cross-functional team, defining a product backlog (a list of features or tasks), and setting up regular sprint cycles. Regular reviews and retrospectives after each sprint will ensure continuous improvement and alignment with stakeholder needs.
-
The Waterfall Project Management Technique
The Waterfall approach is among the pioneering techniques in project management.
In employing the Waterfall method, tasks and activities sequentially progress through five stages:
- Requirements: Gather comprehensive documentation
- Design: Utilize a WBS to itemize tasks
- Implementation: Execute the tasks
- Verification: Evaluate the outcomes
- Maintenance: Sustain and adjust as needed
Who is Waterfall for?
The Waterfall methodology shines in projects with clear-cut stages that demand minimal revisions during the project’s duration. Waterfall might not be the ideal fit if anticipations of frequent scope or budgetary alterations exist.
How to start?
Begin by cataloging all necessary resources and deliverables for every stage. Pivotal to this approach is thorough preparation – especially during the initial phase of project initiation and requirements gathering.
-
Kanban
Kanban boards are graphical tools for task management, consisting of a board with movable cards symbolizing various tasks. They serve as a collaborative platform for project managers and teams, aiding in the visualization of workflows, task allocation, and progress reporting. They’re versatile, benefiting diverse teams from software development to marketing, and even find applications in methodologies like lean manufacturing.
How it functions
Typically, Kanban software divides tasks across columns. A standard Kanban board typically displays three columns indicating task statuses:
- To-do
- Doing
- Done
Why it’s effective
Kanban excels in projects characterized by step-by-step workflows and minimal interdependencies, letting team members focus on their tasks.
-
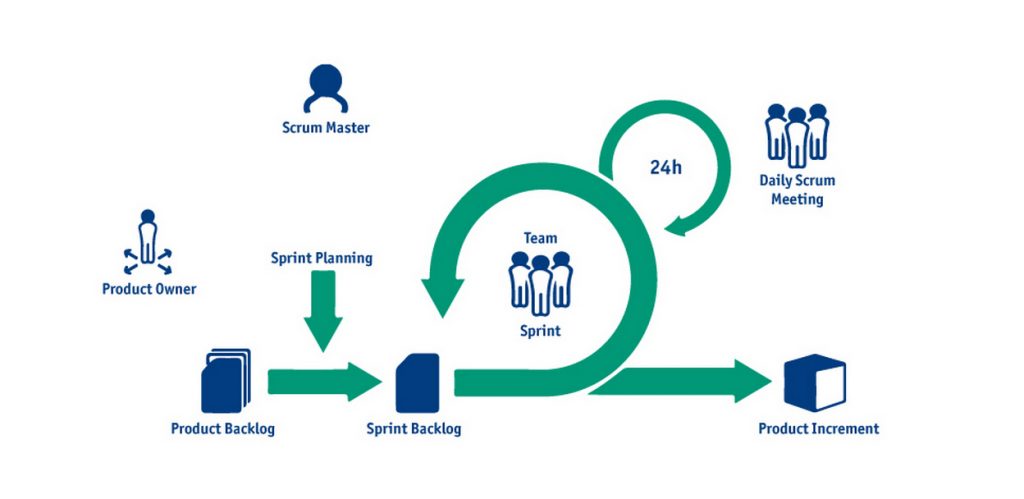
Scrum
Scrum, a prominent Agile methodology technique, is a worthy contender in your pursuit of outstanding project outcomes.
The essence of Scrum lies in its sprints. Each sprint focuses on a distinct deliverable or feature. Typically, sprints should be at most two weeks, punctuated by daily progress check-ins. After completing a sprint:
- Engage in a review session
- Discuss potential enhancements for subsequent sprints
- Proceed
Who’s it for?
Scrum primarily resonates with software development teams and intricate projects, demanding several iterations throughout their duration.
How to start?
Segment the project into individual deliverables or features. Tackle one feature per sprint, aligning them cognizant of task interdependencies.
-
Risk Matrix
The risk matrix stands as a fundamental tool in the project management realm. It offers a straightforward way to evaluate the probability and potential impact of potential project hazards. By assessing risks this way, their influence on the project becomes charitable. Consequently, managers can prioritize these risks and strategize their response if they materialize during the project’s course. Hence, incorporating tools like a risk matrix or log is indispensable for project planning, irrespective of your chosen project management approach.
Commonly encountered risks encompass strategic, operational, financial, technical, and external threats. It’s crucial to note that not all risks are detrimental; some present opportunities that can be leveraged for the project’s benefit.
Who’s it for?
The risk matrix is designed for project managers, stakeholders, and any team involved in project planning and execution. Its utility spans across industries, making it essential for those seeking to address uncertainties preemptively.
How to embark?
Initiate by listing down potential risks associated with the project. Classify each risk based on its likelihood of occurrence and the severity of its impact. Arrange these classified risks on the matrix, and you’ll gain a visual representation to guide your risk management strategies.
-
Critical Path Method (CPM)
The Critical Path Method (CPM) is a pivotal technique in project management, aiding in precisely scheduling all project tasks.
In essence, you’ll be determining the critical path – the most direct route to completing the project – and aligning tasks based on this path. It’s an efficient method for highlighting task dependencies.
CPM allows for the formulation of three duration forecasts for task completion:
- Minimum duration
- Probable duration
- Maximum duration
Who’s it for?
While CPM shines brightest in complicated projects with numerous task interdependencies, its utility isn’t restricted solely to project management methodologies. Like WBS and Gantt Charts, CPM can also be a valuable tool.
How to start?
Begin by itemizing all requisite tasks. Subsequently, pinpoint task dependencies (e.g., Task B can only commence after Task A’s completion) and sketch diagrams to illustrate varying duration predictions.
-
PERT Project Management Technique
PERT, which stands for Program Evaluation and Review Technique, is a strategy in project management designed for refining time estimations. Proper scheduling is pivotal not only for timely project completion but also for adhering to budget constraints.
So, what’s the essence of PERT? It delves into probability, employing network illustrations and foundational statistical approaches. PERT dissects tasks into granular activities, often leveraging the previously mentioned WBS, and then incorporates them into a PERT chart. This process discerns interdependent activities. The resulting data forms a visual representation of the interconnected activity network.
Who’s it for?
PERT is particularly beneficial for project managers and teams handling complex projects where accurate time estimation and sequencing of activities are essential, especially in fields where uncertainty is a significant factor.
How to start?
Start by detailing all project activities and using tools like WBS to dissect them further. Next, map these activities onto a PERT diagram, identifying interdependencies. You can derive the sequence, durations, and slack times from this.
-
Projects IN Controlled Environments (PRINCE2)
Projects IN Controlled Environments (PRINCE2) is a process-driven project management methodology that emphasizes dividing projects into easily manageable and controllable stages.
In PRINCE2, projects are broken down into stages, each with its processes to follow. This ensures clarity on what must be done at every point, by whom, and when. Another distinctive feature of PRINCE2 is its built-in flexibility, which makes it adaptable to all kinds of projects, regardless of size or nature.
Who’s it for?
PRINCE2 is suitable for organizations and project managers who prefer a detailed, process-driven approach to project management. Given its versatility, it can be used in various industries and project sizes.
How to start?
To implement PRINCE2, one should ideally undergo formal training and achieve certification. Begin by understanding its seven principles, themes, and processes. After that, tailor the methodology to fit the specific requirements of your project environment. It’s also recommended to use official PRINCE2 templates and checklists to ensure adherence to its standards.
Conclusion
Choosing the right Project Management Technique for your venture is paramount. Before diving into the complexities of any project, carefully consider which methodology aligns best with your objectives and the nature of the work at hand. The chosen technique can significantly amplify the outcomes when paired with the appropriate tools and best practices. By adhering to the foundational principles of your selected Project Management Technique, you expedite the workflow, ensure meticulous control over project operations, and refine the entire management process.
Furthermore, to further elevate your project management skills and expertise, consider pursuing a PMP Certification through Invensis Learning. Such certifications validate your capabilities and empower you with advanced knowledge and methodologies, ensuring you’re always at the forefront of effective project management.