Every business has to equip best practices in order to optimize the customer demands for each of the services. Demand management in ITIL is one such concept that takes care of the demand from the customers efficiently. The systematic analysis and progressive overload on various services and demands help the businesses fulfill the customer requirements in the most profitable scenario.
ITIL Demand Management
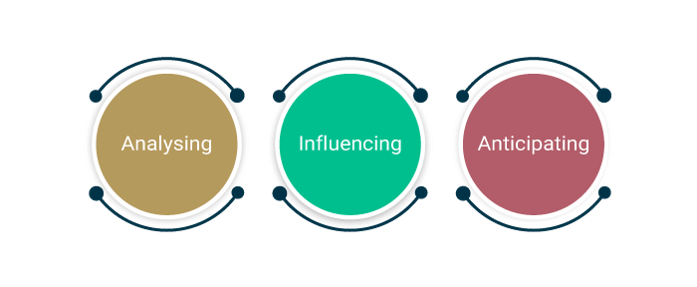
The demand for a particular service can increase or decrease depending on the customer requirements and the market scenario. The main purpose of the demand management process is to analyze, anticipate and influence the demand by the customers for services and the process by which adequate capacity to satisfy the demand is provisioned.
This involves the following actions:
- Analyzing the present usage of IT services by customers
The simplest way to analyze the current customer usage is to analyze the service desk data which contains details of incidents, requests, and problems.
- Anticipating the future demands for IT services by customers
Business relationship management plays a role in anticipating the future demands for IT services by customers. The manager may speak with the customer directly regarding the needs which have been predicted, analyze trends in usage and make educated projections regarding usage of the service in the future based on similar customer trends.
- Influencing the consumption of services as required by technical or financial means
It is the duty of demand management to make sure that the appropriate costs are included in the service design. For example, if a customer makes use of more than the anticipated amount of service as per the Service Level Agreements, then the service provider can charge an additional fee to offset the costs of the unexpected demand.
Objectives of ITIL Demand Management
The objectives of demand management are:
-
Identify and analyze the patterns of business activity (PBA) in order to understand the levels of demand which will be placed on service.
-
To analyze the profiles of the different users of each service so that the profiles of demand can be understood.
-
Make sure that the services are defined to meet the expected patterns of business activity.
-
To ensure that suitable resources are available to meet the demands of the service, which can be achieved by cooperating closely with capacity management.
Scope of Demand Management in ITIL
The main scope of demand management is to identify and analyze the patterns of business activity which initiate the demand for services and identification and analysis of how the different types of users initiate the demand for services.
The scopes of demand and capacity management tend to overlap since demand management is an aspect of capacity management. Both these processes are concerned with achieving the same business outcomes and optimizing the investment made. Demand management has its focuses on the business and user aspects of service provision while service management has its focuses on the aspects of resourcing and technology.
The following should be included in demand management activities:
-
Identification and analysis of the patterns of business activities that are associated with the services.
-
Identification of the user profiles and analyzing their usage patterns in service.
-
To identify, agree to and implement the measures which can influence demand along with capacity management. This is usually known as ‘management of demand.
Demand Prognosis of Demand Management
The business relationship manager analyzes the consumption of IT service and also forecast future consumption based on known information such as consumer trends and feedback from the customer.
In ITIL, when the customer will directly indicate when they are in need of a larger number of services, it is called a Pattern of Business Activity (PBA).
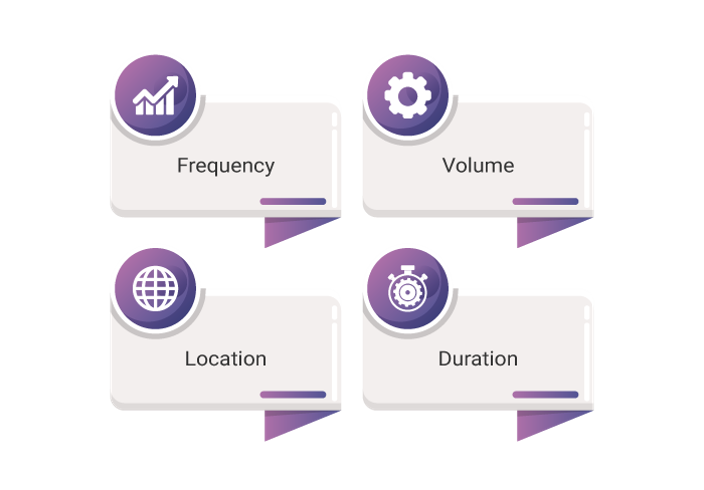
The pattern of Business Activity is a workload profile of one or more business activities that help service providers to establish usage patterns. The following aspects of customer service usage are measured by the pattern of business activity:
- Frequency: It shows how often the volume of usage happens.
- Volume: It shows the amount of activity, and it can increase or decrease.
- Duration: It shows how long the business usage pattern lasts.
- Location: It shows where the business user has occurred.
Demand Control
Demand control is the method by which IT service consumption is controlled by IT service providers. It is done through technical means such as network throttling or financial means such as an increase in charges for greater than agreed-upon levels of usage.
Demand control is applied until the capacity for increased demand is integrated into the service catalog. Demand control can also be implemented by differentiating offerings and service packages. These can control demand and cost while simultaneously providing the customers with the services they need the most.
Value of Demand Management in ITIL
- Demand management is vital because it is impossible to plan adequately to meet increased service demands based on guesswork alone.
- Accurate analysis is made from the data gathered and client feedback received during the demand prognosis stage.
- The major value provided by demand management is that it achieves a balance between the cost of service and the value of a balance it supports.
- Demand management also improves the understanding of how, when, and to what level the elements such as business outcomes, services, resources, and capabilities interact.
- This understanding helps executives to evaluate the actual investment which is required to achieve business outcomes at different levels of activity.
Principles & Basic Concepts of Demand Management in ITIL
-
Supply and demand
-
Consumption produces demand and production consumes demand in a highly synchronized pattern.
-
This demand and supply cycle will function effectively only while the service assets have capacity available.
-
A significant part of demand management is understanding the potential demand and the impact of the demand on the service assets.
-
-
Gearing Service Assets
-
The balance between demand and supply can be achieved by gearing the service assets to meet the dynamic patterns of on-demand services.
-
This is done by responding to demand as it occurs and anticipating the demand by identifying the signals of increasing or decreasing demand.
-
A mechanism should be defined to scale investment and supply as and when required.
-
Managing service assets as per demand variations involves a number of actions by service management:
-
Identifying the services in question through service portfolio management.
-
Quantifying the pattern of business activity
-
Mentioning specifically the appropriate type of architecture to deal with the type and quantity of demand.
-
Capacity and availability are planning to make sure that the assets of the right service are available at the right time and are performing at the right levels as per requirement.
-
Performance management and tuning of service assets to deal with demand variations.
-
-
-
Demand Management Through the Lifecycle
-
Demand management needs to be active throughout the service lifecycle to be fully effective.
-
It should not be assumed that the process which is active at each stage of the lifecycle will address the issues related to demand.
-
If demand management is not coordinated and managed on a regular basis, it will happen only on a reactive basis.
-
ITIL Demand Management Process
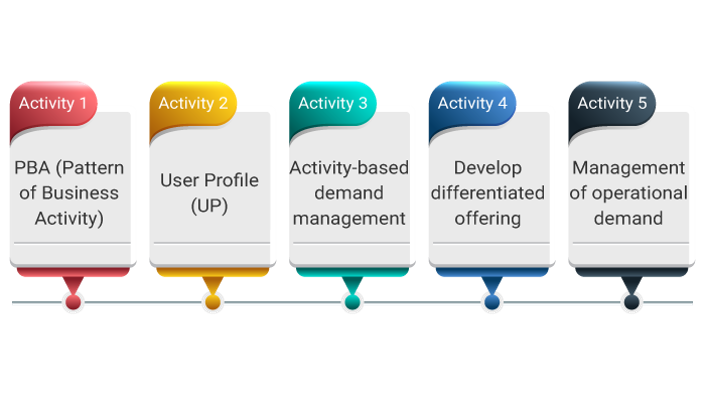
The following process activities and methods can be applied when required to perform ITIL demand management:
-
PBA (Pattern of Business Activity)
The pattern of business activity represents the dynamics of the business and includes interactions with customers, suppliers, partners, and other stakeholders.
-
User Profiles (UP)
Each User Profile can be associated with one or more patterns of business activity based on roles and responsibilities within the organization. User profiles are constructed using one or more predefined patterns of business activity.
When demand is defined using a pattern of business activity and user profiles, service providers can serve demand with services, service levels, and assets that are matched appropriately.
-
Activity-based Demand Management
By analyzing and tracking the activity patterns of business, the demand for IT services that support the process can be predicted.
Activity-based demand management can consolidate demand patterns and ensure that the customer’s business plans are in sync with the capacity management plans.
-
Develop Differentiated Offerings
Analyzing the pattern of business activities may help to identify that varying levels of performance are required at different times.
In such cases, it is important to work along with service portfolio management to define the service packages which meet the variations in the patterns of business activity.
-
Management of Operational Demand
This involves managing or influencing the demand where services and resources are being utilized over the limit.
Challenges of Demand Management in ITIL
The following challenges are faced by demand management:
-
The limited availability of information about business activities especially if demand management is not included in the total set of requirements and information has to be gathered separately.
-
It may be difficult for customers to break down individual activities which make sense to the service provider.
-
A lack of a formal service portfolio or service portfolio management process will make it difficult to understand the business requirements, relative value, and the priority of services.
Risks of Demand Management in ITIL
The following risks are faced during the implementation of demand management:
-
If service demand is poorly managed, it can be a massive risk to the organization
-
If the planning for increases in service usage is not adequate, it can result in service levels being missed. And, poor quality of services across the entire service catalog.
-
Businesses can suffer financial losses, and in some scenarios, the business could be lost altogether if service demand is improperly managed.
Conclusion
The challenges of unprecedented and incomplete information on service demands can be quite a challenge, but effective demand management can plan ahead of the events to overcome such challenges. Learn more about such skills and best practices in service management with ITIL 4 Foundation certification training, and grow in your service management career.
Know more about Service Management best practices through Invensis Learning’s IT Service Management certification training on ITIL 4 Foundation Online Course, SIAM Foundation, SIAM professional, VeriSM, etc.