ITIL Service Operation serves the objective of ensuring the delivery of IT services efficiently in an organization. To ensure the consistent flow of effective IT services, the ITIL service Operation functions and processes are used. In this article, we will learn about ITIL service Operation objectives, scope, functions, processes, etc.
Purpose of ITIL Service Operation
The main objective of IT service operations is to ensure that the required IT services are delivered efficiently and effectively as per the service level agreements to the business users and customers.
Service operations are vital for an organization as a meticulously designed and implemented process will be rendered ineffectual if the operations are ineffectively conducted.
Service operation also helps to improve the service as periodic activities for performance monitoring, assessment metrics, and data gathering are systematically conducted.
Scope of ITIL Service Operation
The following come under the scope of Service Operation
- The service provided by the service provider, external supplier, or even the end-user comes under the scope of service operation.
- Service management also comes under the purview of Service Operation as it provides input and influences service design, strategy, and transition.
- Management of technology is an important part of service operations as all IT services need some form of technology to function.
- Human resource is vital as it is the people who manage the services, technology and take the organization forward. Failure to recognize the importance of a skilled workforce will result in the failure of projects.
Business Value of ITIL Service Operation
In the ITIL service lifecycle, each stage adds some value to the business involved. Service strategy, service design, and service transition play a major role in providing value to a service, but it is only in the service operations stage that the actual value imparted is visible. The values are visible through processes of a service operation such as incident management, event management, problem management, access management, and request fulfillment.
Optimization of ITIL Service Operation
There are 2 ways to optimize service operation.
Long-Term Incremental Improvement
It involves the evaluation of the performance and output of all the processes and functions of service operations over time. All the reports are analyzed, and decisions are made regarding the necessity and type of improvement needed.
For example, changes or reconfiguration of process designs and infrastructure are considered as long-term incremental improvements.
Short-Term Ongoing Improvement
It is concerned with smaller improvements in working practices in the service operation processes without any major change to a process or technology.
For example, reassigning personnel, balancing workload, and refining a process.
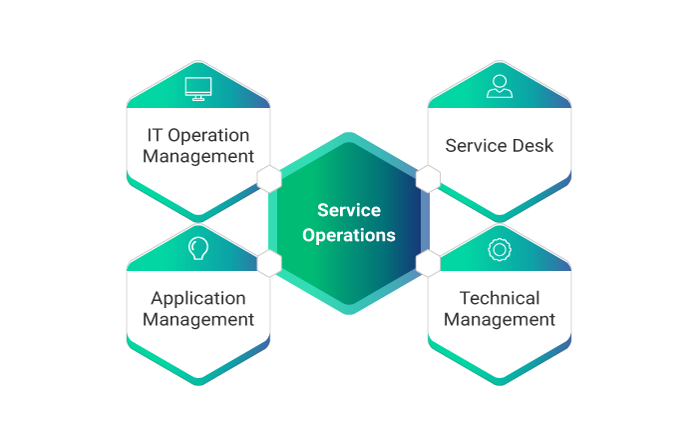
Functions of ITIL Service Operation
There are 4 functions under service operations:
1. Service Desk
The service desk is the primary point of contact for the coordination of activities between the end-user and the IT service provider.
2. Technical Management
The role of technical management is to provide the required in-depth resources and technical skills which are necessary to support the continuing operations in the IT sector of the organization. It is their duty to assist in designing, testing, and releasing new services and improving the existing services.
3. IT Operation Management
The IT Operations Management is in charge of executing the operational activities needed on a day-to-day basis to manage the IT infrastructure in the organization.
4. Application Management
The Application management is responsible for making decisions such as whether to make or buy a service and to play a major role in designing, testing, and improvement of applications.
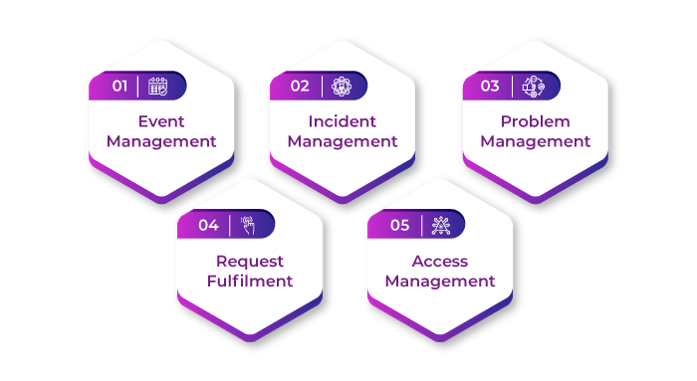
Processes Under Service Operation
1. Event Management
It deals with managing an event through its life cycle. It involves detection of events, filtering them, responding to, and logging them to maintain a record.
2. Incident Management
It is concerned with restoring the disrupted services quickly and bringing them back to normal functioning levels to minimize the impact of the disruption on the business.
3. Problem Management
Problem management deals with finding out the root cause of the incidents and taking proactive measures to ensure that such incidents don’t occur in the future.
4. Request Fulfilment
It deals with service requests, which are small and low-risk changes such as the creation of new user IDs, password changes, etc. which are not the core business of a company.
5. Access Management
Access management is concerned with granting access to use a service to only authorized users and preventing unauthorized ones from accessing them.
Conclusion
IT service operations, thus ensure that the required IT services are delivered efficiently and effectively to the business users and customers since they are vital for the working of an organization. In addition, they improve the service by periodically monitoring the activities, assessing the metrics, and systematically gathering data.
Learn more about Service Management best practices through Invensis Learning’s IT Service Management certification training on ITIL 4 Foundation, SIAM Foundation, SIAM professional, VeriSM, etc.