Ready to ace your Quality Manager interview? In today’s competitive landscape, nailing the interview is more important than ever. You need to showcase not only your technical expertise but also your leadership skills, problem-solving skills, and ability to navigate the ever-evolving world of quality management.
But where do you start? With Top 30 Quality Manager Interview Questions in 2024, your one-stop guide to interview preparation! We’ve compiled most of the beginner, intermediate, and advanced questions hiring managers are asking, along with pro tips and sample answers to help you shine. Don’t let the perfect job slip through your fingers. Grab this power-packed guide, prepare like a pro, and walk into that interview with confidence!
Table of Contents:
- Quality Manager Interview Questions-Beginner Level
- Quality Manager Interview Questions-Intermediate Level
- Quality Manager Interview Questions-Advanced Level
- Conclusion
Quality Manager Interview Questions-Beginner Level
Nervous about your first Quality Manager interview? Take a deep breath! “This beginner-level interview question of a Quality Manager” is your stress-busting guide to overcoming those early career hurdles.
In this section, we lay the foundation by dissecting fundamental questions tailored for beginners. From the basics of quality assurance to the essentials of problem-solving, these questions are designed to evaluate your current knowledge and set the stage for your growth as a Quality Manager.
We’ll equip you with clear answers and confidence-boosting tips, even if you’re starting out.
1. Tell me about your understanding of “Quality Management.”
Quality management is all about ensuring products and services meet or exceed customer expectations. It involves a comprehensive set of principles, methodologies, and tools aimed at planning, controlling, and improving quality throughout the entire lifecycle of a product or service.
Key aspects include:
- Defining quality objectives,
- Implementing robust processes
- Conducting thorough inspections and testing,
- Continuously seeking opportunities for improvement
2. Tell me about your understanding of “Quality Management.”
Quality Control (QC) is a systematic process to ensure that products or services meet specified standards and customer expectations. It encompasses a range of activities, including statistical analysis, inspections, and control charts to maintain consistency and meet predetermined quality criteria. The goal of Quality Control is to minimize errors, enhance product or service reliability, and ultimately satisfy customer requirements.
3. What motivated you to pursue a career in Quality Management?
You can catch the recruiter’s attention by answering this question: I have always been delighted by the idea of ensuring that products or services meet the highest standards. Quality Management allows me to play a crucial role in maintaining and improving the overall quality of processes and deliverables. I find satisfaction in contributing to an organization’s success by ensuring customers receive products or services that meet or exceed their expectations.
4. Describe the difference between verification and validation
Verification and validation are two distinct processes in quality management, each serving a specific purpose in ensuring product or service quality.
The major differences between them are:
Verification:
- Confirms compliance with specified requirements during development.
- Involves activities like reviews, inspections, and audits.
- Focuses on adherence to specifications.
Validation:
- Ensures the end product meets customer needs and functions as intended.
- Conducted post-development through testing and assessments.
- Focuses on the final product’s performance and alignment with user expectations.
What are some key quality control tools and techniques?
5. What are some key quality control tools and techniques?
Quality control tools and techniques are essential in ensuring that products and processes meet established standards.
Here are some key quality control tools and techniques commonly used in various industries:
- Checklists: Ensure task consistency and completeness.
- Flowcharts: Visualize and analyze process workflows.
- Histograms: Display data distribution patterns.
- Control Charts: Monitor process stability over time.
- Fishbone Diagrams: The Fishbone diagrams Identify and categorize root causes of issues.
6. What role does documentation play in Quality Management, and why is it important?
Documentation is a crucial aspect of Quality Management as it establishes, communicates, and maintains quality standards within an organization. Proper documentation includes quality policies, procedures, work instructions, and records of inspections and tests. It provides a reference point for employees, ensuring process consistency and facilitating training. Documentation is also instrumental in audits and assessments, enabling organizations to demonstrate compliance with quality standards and regulations.
7. What are your strengths and weaknesses as a potential Quality Manager?
Be honest and self-aware while answering this question.
As a potential Quality Manager, my strengths lie in strong analytical skills, meticulous attention to detail, effective communication, adaptability, and fostering team collaboration. I excel in problem-solving and thrive in dynamic environments.
On the flip side, I acknowledge the need for improvement in time management to avoid overcommitting, refine delegation skills, and develop resilience in handling constructive criticism. I am actively addressing these weaknesses to enhance my effectiveness in ensuring and maintaining high-quality standards.
8. Explain the key principles of Quality Management according to ISO 9001
The key principles of Quality Management according to ISO 9001 are foundational concepts that guide organizations in achieving and maintaining high-quality standards. These principles provide a framework for developing and implementing effective quality management systems. The key principles include customer focus, leadership, engagement of people, process approach, improvement, evidence-based decision-making, and relationship management.
9. How do you motivate your team to meet and exceed quality standards consistently?
I motivate my team through recognition, positive reinforcement, and a culture of continuous improvement. Celebrating individual and collective achievements, providing tangible rewards, and fostering open communication channels contribute to their motivation. Regular feedback sessions ensure that team members feel valued and heard, promoting a sense of ownership. Involving them in decision-making processes strengthens their commitment to quality outcomes. This approach creates a collaborative and supportive atmosphere, driving the team’s engagement and dedication to consistently exceeding quality standards.
10. Can you share an experience where you contributed to improving quality in a previous role, even if you were not in a quality-specific position?
In a previous role where I wasn’t explicitly in a quality-specific position, I identified a recurring issue affecting product quality. Recognizing the importance of addressing it, I proactively initiated a cross-functional collaboration involving relevant departments. Together, we conducted a thorough root cause analysis, identifying process gaps leading to the quality issue.
Despite not being in a designated quality role, I played a key part in implementing process improvements. This experience emphasized the value of a proactive approach to quality improvement and showcased my commitment to ensuring and enhancing overall product quality.
Quality Manager Interview Questions-Intermediate-Level
Quality Managers are pivotal in ensuring organizations deliver products and services that meet or exceed customer expectations. As professionals responsible for maintaining high standards, they navigate complex processes, implement robust quality management systems, and lead teams toward continuous improvement.
In an intermediate-level Quality Manager interview, candidates are expected to showcase a deep understanding of quality principles, problem-solving skills, and the ability to drive an organization’s excellence culture.
These questions measure candidates’ ability to navigate complex challenges, implement effective quality management systems, and foster a culture of excellence within their teams and organizations.
11. Describe your management style as a Quality Manager
This question is an opportunity to showcase your leadership approach and ability to guide a team towards consistently achieving quality goals.
Here’s how you can explain your management style effectively:
- Identify your core values
- Provide concrete examples
- Tailor your answer to the company and role
- Be authentic and transparent
Here’s an example answer:
My management style revolves around data-driven decision-making, continuous improvement, and empowering my team. In my previous role, I implemented a Six Sigma project to reduce production defects. I involved my team in identifying root causes and developing solutions, which led to a 20% decrease in defect rates.
I believe in creating an open and supportive environment where everyone feels accountable for quality and empowered to contribute their ideas. While I excel at leading by example, I’m constantly seeking feedback and open to adapting my approach to best suit the team and the situation.
Remember, the key is to be clear and concise and provide concrete examples that demonstrate your leadership skills and commitment to quality excellence.
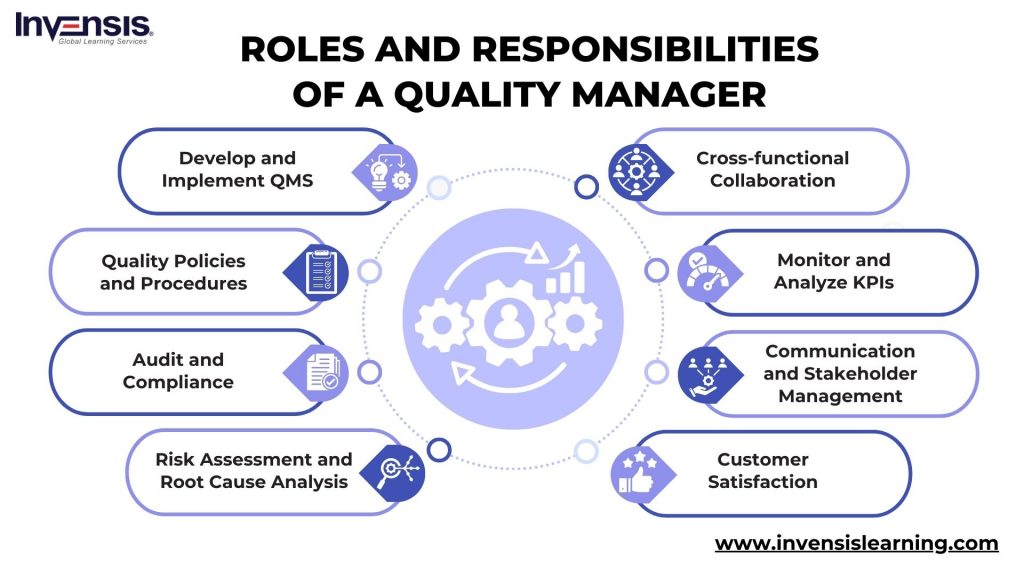
12. What are the roles and responsibilities of a Quality Manager?
As a Quality Manager, the roles and responsibilities are multifaceted and pivotal to ensuring an organization’s overall quality and compliance.
Candidates can answer this question by highlighting their duties like:
Develop and Implement QMS
- Design, implement, and maintain the Quality Management System (QMS).
- Ensure adherence to regulatory requirements and organizational standards.
Quality Policies and Procedures
- Develop and enforce quality policies, procedures, and standards.
- Regularly review and update the documentation to reflect best practices.
Audit and Compliance
- Plan and execute quality audits and assessments.
- Identify areas for improvement and ensure compliance with quality standards.
Risk Assessment and Root Cause Analysis
- Conduct risk assessments to identify potential quality-related risks.
- Perform root cause analyses and implement corrective and preventive actions.
Cross-functional Collaboration
- Collaborate with cross-functional teams to align quality objectives with organizational goals.
- Engage in training programs to ensure team members understand and adhere to quality standards.
Monitor and Analyze Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
- Monitor and analyze key performance indicators (KPIs) to assess the effectiveness of quality processes.
- Implement continuous improvement initiatives based on KPI insights.
Communication and Stakeholder Management
- Communicate internally with team members and externally with stakeholders to ensure transparency.
- Align on quality goals and foster a culture of excellence.
Customer Satisfaction
- Monitor and enhance customer satisfaction with products or services through quality initiatives.
- Respond to customer feedback and implement improvements as necessary
13. What should be a Quality Manager’s daily routine?
A Quality Manager’s daily routine is dynamic and involves a combination of strategic planning, operational oversight, and continuous improvement efforts.
Typically, the daily responsibilities include:
- Start the day by reviewing any urgent emails, messages, or updates to stay informed about immediate issues or changes
- Conduct a brief team check-in to discuss priorities, ongoing projects, and any emerging quality issues
- Regularly monitor key quality metrics and performance indicators
- Conduct routine inspections or assessments of ongoing processes to ensure compliance with quality standards
- Dedicate time to ongoing continuous improvement initiatives
This routine ensures the Quality Manager’s active involvement in strategic planning, daily operations, and continuous improvement efforts.
14. How would you explain the Project Quality Management process, according to PMBOK?
This question assesses your understanding of the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK) and its application to quality management within projects. Here’s how you can impress the interviewer:
The PMBOK outlines a Quality Management process encompassing various standards, providing a valuable guide for Quality Managers in successfully delivering projects and products.
It offers step-by-step guidance for Quality Managers to ensure project compliance effectively. The Project Quality Management process in PMBOK is structured around three main processes:
- Quality Planning
- Quality Assurance
- Quality Control
Quality Planning involves the establishment of quality metrics. Quality Assurance focuses on the analysis and ongoing improvement of both production and project processes.
15. Discuss your experience implementing a specific quality management methodology (e.g., Six Sigma, Lean, Agile)
This question delves deeper into your practical experience applying quality management principles. To impress the interviewer, tailor your answer to the specific methodology they mentioned (e.g., Six Sigma) and showcase your:
In a previous role, I spearheaded the implementation of Six Sigma methodologies to enhance overall process efficiency and product quality. This initiative involved several key components:
- Define Phase: Collaborated with cross-functional teams to clearly define project goals, objectives, and customer requirements. Established measurable metrics to gauge success.
- Measure Phase: Conducted comprehensive data analysis to identify areas for improvement. Utilized statistical tools to assess process performance and variability, laying the groundwork for targeted improvements.
- Analyze Phase: Employed root cause analysis techniques to identify underlying issues affecting quality. Collaborated with team members to discover data trends and determine the most impactful improvement opportunities.
- Improve Phase: Implemented process modifications and enhancements based on the findings from the Analyze phase. Worked closely with team members to ensure seamless integration of changes while considering efficiency and resource optimization.
- Control Phase: Developed and implemented control measures to sustain the improvements achieved. Established monitoring systems to track ongoing performance and promptly addressed deviations from the enhanced processes.
16. How do you measure the effectiveness of your quality management system?
Measuring the effectiveness of a quality management system (QMS) is critical to ensuring continuous improvement and alignment with organizational goals. I employ a multifaceted approach that involves the following key components:
- Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Monitor specific KPIs aligned with quality objectives for quantitative insights.
- Internal Audits: Conduct regular internal audits to identify non-compliance or improvement opportunities.
- Customer Feedback: Analyze customer feedback to understand perceived quality and areas for enhancement.
- Continuous Improvement Metrics: Assess the impact of improvement initiatives and changes made to enhance processes.
- Process Performance Analysis: Analyze process efficiency, consistency, and adherence to quality standards.
- Compliance Audits: Verify adherence to industry standards, regulations, and legal requirements.
Bonus Tip: Showcase your knowledge of specific quality management standards or frameworks, like ISO 9001, and how their measurement requirements inform your approach.
17. Can you explain the concept of Total Quality Management (TQM) and its relevance in today’s business environment?
Total Quality Management (TQM) is a comprehensive management concept that emphasizes continual improvement, customer happiness, and employee engagement across a business. TQM highlights the necessity of taking a systematic approach to quality and involves all employees in the pursuit of excellence.
TQM is relevant in today’s dynamic business world because it provides a framework for firms to adapt to changing market conditions, optimize processes, and increase overall customer satisfaction.
Employee empowerment, data-driven decision-making, and a dedication to excellence are all TQM values that connect with today’s corporate goals of agility, innovation, and customer focus. TQM allows firms to remain competitive, respond effectively to market needs, and establish a reputation for providing high-quality products and services by cultivating a culture of continuous improvement.
18. What steps would you take to identify and address the root causes of recurring quality issues?
This question assesses your problem-solving abilities and commitment to continuous improvement.
Impress the interviewer by outlining a logical, data-driven approach:
- Gather Data and Define the Problem
- Start by clearly defining the recurring quality issue, using specific data and metrics to quantify its impact.
- Gather all relevant data about the issue, including production records, inspection reports, and customer feedback.
- Analyze and Prioritize
- Use data analysis tools like Pareto charts or root cause analysis (RCA) methods to identify the most frequently occurring causes and their potential impact.
- Prioritize your investigation based on the severity of the issue and its impact on customer satisfaction or production costs.
- Deep Dive into Causes:
- Conduct a thorough investigation of the prioritized causes, utilizing specific techniques like 5 Whys: Ask “why” repeatedly to uncover the underlying logic behind each cause.
- Fishbone Diagram: Visually map out the potential contributing factors and their relationships.
- Process Observation and Interviews: Gain firsthand insights by observing the relevant processes and interviewing involved personnel.
- Identify the True Root Cause
- Don’t stop at the immediate cause. Keep digging until you reach the underlying root cause, which triggers the chain of events leading to the quality issue.
- Develop and Implement Solutions
- Based on the identified root cause, develop targeted corrective actions to address the issue at its source.
- Implement these solutions effectively, ensuring proper training and communication for all affected personnel.
- Monitor and Evaluate
- Track the effectiveness of your implemented solutions through continuous data analysis and monitoring.
- Be prepared to adapt and adjust your approach based on the evaluation results if necessary.
19. Explain your approach to implementing a new Quality Management System (QMS) within an organization
Implementing a new Quality Management System (QMS) is a multifaceted process that requires a strategic and systematic approach.
This question assesses your leadership, planning, and communication skills within the context of QMS implementation.
Impress the interviewer with a structured and thoughtful answer:
- Assessment and Understanding: Conduct a thorough assessment of the organization’s current state, including existing processes, documentation, and quality practices.
- Stakeholder Engagement: Engage key stakeholders across various departments to ensure their involvement and alignment with the new QMS.
- Strategic Planning: Develop a strategic plan outlining the implementation timeline, milestones, and resource requirements.
- Communication: Establish transparent and open communication channels to keep all stakeholders informed about the progress of the QMS implementation.
- Phased Implementation: Implement the new QMS in a phased approach to manage the change effectively. Monitor and evaluate each phase, making adjustments as needed based on feedback and performance metrics.
- Documentation and Compliance: Develop clear and concise documentation for QMS processes and procedures.
- Continuous Monitoring and Improvement: Implement mechanisms for continuous monitoring of the QMS effectiveness through key performance indicators (KPIs) and regular audits.
- Review and Adaptation: Regularly review the QMS to ensure its alignment with evolving organizational needs.
20. How do you communicate complex quality data and insights to stakeholders at different levels?
Effectively communicating complex quality data is essential for ensuring that stakeholders at various levels comprehend and act upon the insights.
My approach involves:
- Tailored Communication: Customize communication for executives and quality professionals, using language that suits their respective levels of technical understanding.
- Visual Representation: Simplify complex data with charts and graphs, facilitating quicker comprehension and enhancing overall accessibility.
- Focus on Key Metrics: Emphasize relevant KPIs for each stakeholder, aligning metrics with organizational goals and objectives.
- Contextualization: Relate data to specific processes or projects, providing context and illustrating its direct impact on the business.
- Regular Reporting and Feedback: Establish a consistent reporting schedule to provide timely updates, accompanied by a feedback mechanism for continuous improvement in communication strategies.
Quality Manager Interview Questions-Advanced Level
In the dynamic landscape of Quality Management, the role of a Quality Manager goes beyond the conventional, requiring a blend of strategic vision, technical expertise, and innovative thinking.
This curated set of advanced-level interview questions aims to evaluate candidates’ proficiency in navigating the complexities of modern industries. From implementing sophisticated quality methodologies to integrating cutting-edge technologies, managing risks proactively, ensuring compliance in regulated sectors, and fostering a culture of innovation, these questions explore the depth of a candidate’s experience and strategic approach to quality management.
The provided answers offer insights into how candidates at the advanced level tackle intricate challenges, showcasing their ability to lead organizations toward unparalleled excellence in quality assurance.
21. What is defect triaging, and what function does the Quality Manager play in it?
Defect triaging is a crucial process in software development and quality assurance to prioritize and manage reported defects or issues. It systematically evaluates, categorizes, and assigns priorities to each reported defect based on its severity, impact, and other relevant factors. The Quality Manager plays a central role in defect triaging by overseeing the entire process. Their functions include:
- Leading the triage team
- Prioritization and classification
- Communication and collaboration
- Resource allocation
- Monitoring and reporting
22. How do you standardize quality processes in a globalized manufacturing environment while accounting for regional variations and compliance requirements?
In a global manufacturing setting, standardizing quality processes involves establishing core standards as a baseline for consistency. To accommodate regional variations, allow flexibility within the standardized framework, enabling customization while maintaining uniformity. Leverage technology for real-time updates, provide ongoing training and ensure compliance with international and regional regulations.
Implement centralized reporting and monitoring, appoint global quality leaders, and encourage a feedback loop for continuous improvement. This strategic approach balances standardization with adaptability, fostering a commitment to quality across diverse regions.
Bonus Tip: Share a relevant example from your experience where you successfully managed a similar challenge in a global environment. This showcases your practical skills and adaptability.
23. As a Quality Manager, how do you decide which QA processes should be manual and which should be automated?
The decision to choose between manual and automated QA processes requires a strategic assessment based on various factors.
Here’s how I approach this decision-making process:
Complexity and Repetitiveness
- Manual Testing: Suitable for tasks requiring human intuition and creativity, especially in exploratory testing.
- Automated Testing: Efficient for repetitive, rule-based tasks, ensuring precision and speed.
Critical Path and Time Sensitivity
- Manual Testing: Appropriate for critical tasks demanding human decision-making or creativity.
- Automated Testing: Effective for time-sensitive tasks requiring quick and consistent execution.
Resource and Skill Availability
- Manual Testing: Depends on skilled human testers, suitable when automation expertise is limited.
- Automated Testing: Efficient when skilled resources are available, enhancing repeatability and speed.
Change Frequency and Stability
- Manual Testing: Adaptable to frequent changes and evolving requirements.
- Automated Testing: Ideal for stable processes, providing faster and consistent results.
Regression Testing
- Manual Testing: Effective for smaller-scale regression testing efforts.
- Automated Testing: Highly efficient for large-scale regression tests, ensuring quick and reliable results.
The decision involves a thoughtful analysis of project requirements, resource capabilities, and the desired outcomes. A balanced approach that combines both manual and automated testing based on the unique needs of each QA process typically yields optimal results.
24. How do you leverage advanced technologies such as blockchain, IoT, or AI to enhance quality processes and outcomes?
Utilizing advanced technologies such as blockchain, the Internet of Things (IoT), and Artificial Intelligence (AI) can significantly enhance quality processes and outcomes.
Here’s how each technology can be applied:
Blockchain:
- Ensures product traceability and transparent supply chain records.
- Automates and enforces quality agreements, reducing the risk of defects.
- Utilizes blockchain for product authentication and anti-counterfeiting.
Internet of Things (IoT)
- Monitors manufacturing processes in real-time for immediate issue identification.
- Uses IoT sensors to predict and prevent equipment failures, reducing downtime.
- Enhances supply chain visibility, monitoring environmental conditions during transportation.
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- Analyzes historical data to predict and prevent potential quality issues.
- Applies AI-powered tools for efficient and complex testing processes.
- Utilizes NLP to analyze customer feedback and identify product quality insights.
25. As a Quality Manager, what best practices will you follow to keep the automation suite up to date?
Maintaining an up-to-date automation suite demands a proactive and vigilant approach.
Here are the best practices I would employ as a Quality Manager:
Regular Maintenance
- Conduct routine automated checks, including daily smoke tests.
- Use version control like Git for effective change tracking.
Monitoring and Adaptability
- Stay vigilant about application changes, promptly update scripts.
- Regularly analyze test results, optimizing scripts based on insights.
Collaboration and Knowledge Sharing
- Foster cross-functional communication and encourage script ownership.
- Organize periodic knowledge-sharing sessions.
Technology and Tooling
- Stay updated on the latest automation tools.
- Integrate with CI/CD pipelines for automated testing.
- Explore cloud-based solutions for scalability and collaboration.
26. Describe a situation where you had to develop and implement an innovative solution to a persistent quality issue.
In a previous role, our team faced a persistent quality issue related to the timely detection and resolution of software bugs during development. Despite utilizing traditional testing methodologies, some issues consistently slipped through to production, causing post-release disruptions.
To address this challenge, I proposed and implemented an innovative solution involving the integration of machine learning (ML) algorithms into our testing process. We leveraged historical data on defects, analyzing patterns and correlations to predict potential vulnerabilities in the codebase.
This approach aimed to proactively identify areas with a higher likelihood of defects, allowing the team to allocate resources more efficiently and focus testing efforts on critical sections of the software.
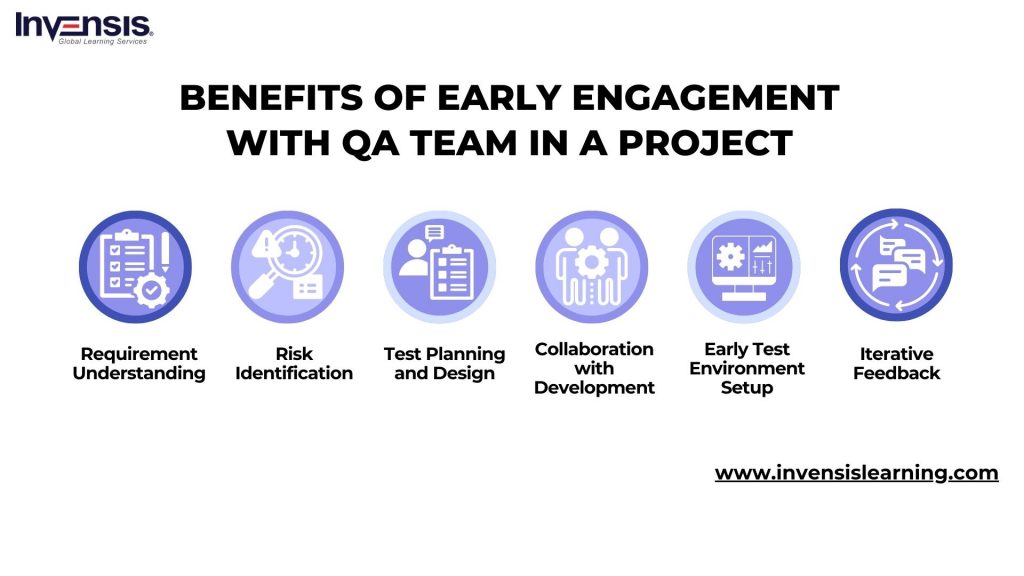
27. When is a good time to start engaging quality assurance team members in a project?
Engaging quality assurance (QA) team members at the right stage is critical for ensuring a smooth and effective project lifecycle. I believe the ideal time to involve the QA team is during the project’s early planning and design phases. Early engagement allows QA professionals to comprehensively understand project requirements, objectives, and design specifications. This involvement facilitates the identification of potential challenges, risks, and testing requirements from the outset.
The key benefits of collaborating with the QA team in the early stages include:
- Requirement Understanding: Active participation in requirement discussions ensures a clear understanding of project goals.
- Risk Identification: Early involvement identifies potential risks, enabling targeted test plans and mitigation strategies.
- Test Planning and Design: Contribution to test planning and design sets the foundation for efficient testing later in the project.
- Collaboration with Development: Early collaboration fosters continuous communication, integrating quality considerations into development.
- Early Test Environment Setup: Initiating the test environment setup early streamlines the testing process and prevents delays.
- Iterative Feedback: Providing iterative feedback throughout the lifecycle contributes to improved code quality and adherence to standards.
28. How would you approach a scenario where conflicting data sets provide different insights into a quality issue?
Conflicting data sets in a quality issue can be frustrating, but it also presents an opportunity for deeper exploration and a more thorough understanding of the problem.
Here’s how I would approach such a scenario:
- Data Validation: Verify sources, collection methods, and potential biases in conflicting data sets for accuracy.
- Collaborative Discussion: Involve cross-functional teams to understand the context and implications of conflicting data.
- Root Cause Analysis: Identify factors contributing to conflicts through a focused root cause analysis.
- Testing Hypotheses: Formulate and test hypotheses to validate or invalidate conflicting data perspectives.
- Consolidation: Synthesize conflicting insights by identifying similarities and patterns.
- Communication Plan: Develop a clear plan to communicate findings, resolutions, and adjustments to stakeholders.
29. What should a Quality Manager do if the defect rate is higher than usual?
A Quality Manager must be able to make decisions and execute them swiftly, particularly when there is a sudden surge or noticeable trends in the defect rate. In such scenarios, it is imperative to analyze the nature of defects or bugs, examine logs, and scrutinize recent changes. Collaboration with the development team or leads for defect triage is essential. Isolating the most recent updates to the application or code with developer assistance is crucial.
Additionally, conducting and documenting a root cause analysis (RCA) and outlining the actions taken are pivotal steps to not only address the current situation but also to plan for preventing similar outcomes in the future.
30. Explain your approach to implementing a culture of innovation within the quality management team. How do you encourage continuous improvement and creative problem-solving?
Implementing a culture of innovation within the quality management team requires a strategic and supportive approach.
Here’s how I would foster an environment that encourages continuous improvement and creative problem-solving:
- Leadership Vision and Support: Secure leadership support and communicate a compelling vision that underscores the importance of continuous improvement and creative problem-solving
- Open Communication: Establish open communication channels, fostering an environment where team members feel comfortable sharing ideas, insights, and feedback
- Recognition for Innovation: Recognize and celebrate innovative efforts regularly to reinforce the value placed on creativity and problem-solving within the team
- Cross-Functional Collaboration: Encourage collaboration between quality management and other departments to bring diverse perspectives and innovative solutions
- Empowerment and Autonomy: Empower team members with the autonomy to explore and implement innovative solutions, fostering a sense of ownership and initiative
Conclusion
In conclusion, the role of a Quality Manager is crucial in ensuring that organizations maintain and improve the quality of their products and processes. The interview questions highlighted in this blog are designed to assess not only candidates’ technical knowledge and skills but also their ability to adapt to evolving industry trends and embrace innovative quality management practices in 2024.
By asking thoughtful and forward-looking questions, hiring managers can identify candidates who meet the current demands of the quality management role and are well-positioned to thrive in the dynamic and ever-changing landscape of 2024.
Ace the interview? Now, become an Agile expert with ease! Invensis Learning’s Quality Management Certification Courses unleash your career potential through industry-aligned training and globally recognized certifications. Elevate your quality game – explore our website and embark on your journey to Agile mastery!