Project failures cost organizations an estimated $122 million for every $1 billion invested, with inadequate risk management identified as a contributing factor in 67% of failed projects, according to research. As projects grow more complex and stakeholder expectations increase, the gap between organizations that use sophisticated risk management software and those that rely on spreadsheets becomes a competitive advantage, or a critical vulnerability.
Traditional risk tracking methods, Excel spreadsheets passed via email, static risk registers reviewed in monthly meetings, reactive rather than proactive risk identification, no longer suffice in today’s fast-paced project environments. Modern risk management demands real-time visibility, predictive analytics, automated workflows, and seamless integration with broader project management ecosystems.
This comprehensive guide examines the best risk management software solutions available in 2026 for project and program managers. You’ll discover detailed comparisons of leading platforms, learn which tools best suit different organizational contexts (from startups to global enterprises), understand critical features to evaluate, and gain a practical framework for selecting and implementing the right solution. Whether you’re managing a single critical project or overseeing a portfolio of complex programs, you’ll find actionable guidance to elevate your risk management capabilities.
Table of Contents
- Why Risk Management Software?
- Key Features to Look for in Risk Management Software
- Top Risk Management Software Solutions
- Software Selection Guide by Organization Size
- Integration Considerations
- Implementation Best Practices
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
Why Risk Management Software?
Limitations of Manual Risk Tracking
Spreadsheet chaos represents the most common pain point for project managers attempting manual risk management. Excel-based risk registers quickly become unwieldy as projects scale. version control nightmares emerge when multiple stakeholders maintain separate copies, critical updates get lost in email threads, and identifying current risk status requires detective work through conflicting spreadsheets.
Lack of real-time visibility means decisions get made based on outdated information. When your risk register was last updated three weeks ago, but circumstances changed yesterday, leadership operates blindly. Manual processes cannot provide the instant visibility modern project velocity demands.
Collaboration difficulties multiply as teams grow geographically distributed. How do team members in three time zones update risks, comment on mitigation strategies, and coordinate responses when the master spreadsheet lives on someone’s laptop? Email attachments and shared drives create information silos rather than enabling collaboration.
Analysis limitations constrain strategic insight. Spreadsheets lack built-in Monte Carlo simulation, probability distributions, schedule impact analysis, or portfolio-level risk aggregation. PMs spend hours creating charts that specialized software generates instantly, and complex “what-if” scenarios require manual recalculation prone to errors.
Benefits of Dedicated Risk Management Tools
Centralized risk registers ensure single sources of truth accessible to all stakeholders with appropriate permissions. Everyone sees the same current data, updates propagate immediately, and audit trails track who changed what and when, critical for compliance and governance.
Automated workflows and alerts transform reactive risk management into proactive monitoring. The software triggers notifications when risks escalate beyond thresholds, reminds owners of pending mitigation actions, and escalates overdue items automatically. PMs focus on strategic decisions rather than administrative chase-down.
Real-time reporting and dashboards deliver instant visibility into risk exposure, trends over time, mitigation effectiveness, and emerging patterns. Executive dashboards summarize portfolio-level risk with drill-down capability into specific projects, enabling data-driven prioritization and resource allocation.
Audit trails and compliance provide automatic documentation of risk management activities, who identified each risk, when mitigation strategies were approved, what changes occurred over time. This traceability satisfies regulatory requirements, supports lessons learned, and protects organizations in litigation scenarios.
| PRO TIP
Don’t invest in dedicated risk management software until you have basic risk management processes established. Software automates and scales existing processes, it doesn’t create processes where none exist. If your organization doesn’t consistently identify, assess, and respond to risks using manual methods, software won’t magically fix that. Start with solid risk management practices using simple tools, then invest in software once you’ve proven the process value and outgrown manual methods’ capabilities. |
Key Features to Look for in Risk Management Software
Essential Features
Risk register and categorization provide the foundational database for capturing and organizing risks. Look for flexible categorization schemes (by project phase, risk type, organizational unit, etc.), custom fields to capture organization-specific information, and powerful search and filtering enabling quick risk identification.
Probability and impact assessment tools should support both qualitative scales (High/Medium/Low) and quantitative analysis (percentage probabilities, monetary impact ranges). Multi-dimensional scoring beyond simple P×I calculations, considering factors such as detectability, velocity, and stakeholder concerns, adds sophistication.
Risk matrix visualization instantly communicates risk exposure through heat maps plotting probability versus impact. Interactive matrices should support filtering, drill-down into specific risks, and scenario comparison to show how mitigation strategies shift the risk profile.
Mitigation planning and tracking transform identified risks into actionable response plans. Features should include: assigning mitigation owners, setting due dates, tracking completion status, documenting contingency plans, calculating residual risk after mitigation, and maintaining a history of what was tried and what worked.
Advanced Features
Monte Carlo simulation enables quantitative schedule and cost risk analysis by running thousands of project scenarios considering probability distributions for uncertain variables. This produces probabilistic forecasts, “80% confidence of completing by this date” rather than single-point estimates, essential for realistic planning and contingency determination.
Integration with project management tools creates powerful synergy. Two-way data sync with Microsoft Project, Primavera P6, or Smartsheet means risks affecting schedule activities automatically update timeline forecasts, and schedule changes trigger risk reassessments. This integration prevents risks from becoming disconnected from project reality.
Custom workflows and approvals enforce organizational governance by routing high-severity risks through approval chains, requiring documented assessments before risk acceptance, and ensuring appropriate visibility at each risk classification level. Workflow engines should be configurable without coding.
Portfolio-level risk aggregation rolls up risks across multiple projects, programs, or business units to provide enterprise visibility. This allows organizations to identify systemic risks affecting multiple initiatives, correlate risks across the portfolio, and make informed prioritization decisions based on overall risk exposure.
Enterprise Features
Multi-project/program support with hierarchical structures enables program managers to see how component project risks aggregate to program-level risks, identify cross-project dependencies that create risks, and manage risks at appropriate organizational levels.
Compliance and audit trails automatically log all risk management activities, creation, modification, approval, closure, with timestamps and user attribution. This satisfies regulatory requirements in controlled industries (pharmaceutical, financial services, aerospace) and provides evidence of due diligence in governance reviews.
API and data integration capabilities allow risk data to flow between enterprise systems, pulling project data from ERP, feeding risk metrics into business intelligence platforms, triggering notifications via collaboration tools. Modern REST APIs enable custom integrations tailored to organizational needs.
Role-based access control (RBAC) ensures appropriate information security, team members see their project risks, PMO views portfolio risks, executives see strategic risks, and auditors access compliance data, without compromising confidentiality of sensitive competitive or personnel information.
Top Risk Management Software Solutions
Enterprise Solutions
- Resolver
Resolver provides a comprehensive Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC) platform with robust risk management capabilities suitable for large enterprises managing complex risk portfolios across business units, projects, and regulatory domains.
Key Features:
- Integrated risk, compliance, incident, and audit management in a unified platform
- Advanced risk assessment frameworks supporting multiple methodologies (COSO, ISO 31000, NIST)
- Powerful reporting with 100+ pre-built templates and a custom dashboard builder
- Workflow automation for risk approval, escalation, and mitigation tracking
- Risk heat maps, bow-tie analysis, and loss event correlation analytics
- Mobile app for field risk assessments and incident reporting
Best For: Large enterprises (500+ employees), regulated industries, organizations needing an integrated GRC platform, program management offices coordinating multiple initiatives
Pricing Model: Custom enterprise licensing based on users and modules; typical implementations $50K-$200K+ annually
Pros: Comprehensive functionality, highly configurable, strong compliance features, excellent vendor support, and implementation services
Cons: Higher cost, complexity requires dedicated administration, longer implementation timelines (3-6 months), may be overkill for single-project needs
- Fusion Framework System
Fusion Framework delivers enterprise-wide risk management (ERM) with emphasis on strategic risk, operational risk, and project portfolio risk integration, popular in infrastructure, construction, and energy sectors.
Key Features:
- Risk-adjusted portfolio prioritization and resource allocation
- Integrated risk, opportunity, and issue management
- Advanced analytics, including Monte Carlo simulation for portfolio optimization
- Customizable risk frameworks aligned to organizational methodology
- Risk-informed decision support for project selection and governance
- Integration with Primavera P6, MS Project, and enterprise PPM systems
Best For: Project-intensive industries (construction, engineering, infrastructure), portfolio management offices, organizations managing $100M+ project portfolios
Pricing Model: Tiered licensing by number of projects and users; typical range $40K-$150K annually
Pros: Strong portfolio analytics, excellent P6 integration, proven in complex project environments, robust training and certification program
Cons: Steep learning curve, best value at portfolio scale (less suited for individual projects), requires significant configuration, interface is less modern than newer competitors
- LogicManager
LogicManager offers a cloud-based ERM platform balancing enterprise capabilities with user-friendly interfaces, growing in popularity among mid-to-large organizations seeking modern GRC solutions.
Key Features:
- Intuitive risk register with drag-and-drop interface and visual risk mapping
- Automated risk assessment workflows with questionnaire builder
- Real-time dashboards and executive reporting with drill-down analytics
- Integration marketplace connecting to 50+ enterprise applications
- Mobile-responsive design enabling risk management anywhere
- Vendor risk assessment and third-party risk management modules
Best For: Growing mid-market (200-2,000 employees), organizations modernizing from legacy GRC tools, companies prioritizing user adoption and ease of use
Pricing Model: Subscription-based, per-user pricing; typically $25K-$100K annually depending on users and modules
Pros: Modern interface drives high adoption, faster implementation (4-8 weeks typical), strong customer success support, transparent pricing
Cons: Less depth than Resolver in certain specialized compliance areas, newer vendor (less track record), advanced analytics less sophisticated than specialized project risk tools
Project Management-Integrated Solutions
- Active Risk Manager (ARM)
Active Risk Manager, developed by Arm Project Management, specializes in project and program risk management with deep integration into project scheduling and cost management tools.
Key Features:
- Probabilistic schedule and cost analysis using Monte Carlo simulation
- Native integration with Primavera P6, MS Project, and Safran for schedule risk
- Risk-adjusted earned value management tracking cost and schedule performance
- Mitigation tracking linked to project schedules showing implementation progress
- Risk allocation and contingency management for project budgets
- Multi-language support for global program teams
Best For: Complex projects with detailed schedules (construction, aerospace, defense, pharmaceuticals), program managers needing schedule risk analysis, PMO standardizing risk methodology
Pricing Model: Perpetual licenses ($3K-$6K per license) or subscription ($1.2K-$2K annually); volume discounts available
Pros: Industry-leading schedule risk analysis, excellent MS Project and P6 integration, comprehensive training resources, proven in major capital projects
Cons: Windows-only (no web or Mac version), interface feels dated, steep learning curve for advanced analytics, requires Primavera P6 for maximum value
- RiskyProject
RiskyProject by Intaver Institute focuses on quantitative schedule and cost risk analysis, particularly popular among project managers in construction, IT, and product development.
Key Features:
- Integrated schedule risk analysis with Gantt chart view and critical path identification
- Risk-adjusted schedule baselines showing probabilistic completion dates
- Cost risk analysis with cumulative probability curves (S-curves)
- Sensitivity analysis identifying highest-impact risks on schedule and cost
- Custom probability distributions for activity durations and costs
- Risk response strategy modeling showing mitigation ROI
Best For: Project managers needing schedule-centric risk analysis, organizations transitioning from basic risk registers to quantitative analysis, technical project leaders comfortable with statistical concepts
Pricing Model: Perpetual licenses starting at $850 for Professional version, $1,800 for Enterprise; annual maintenance 20% of license cost
Pros: Affordable entry point for quantitative analysis, good balance of functionality and usability, standalone tool (no complex infrastructure), free trial available
Cons: Limited collaboration features, basic reporting compared to enterprise tools, Windows-only, doesn’t replace full risk register for qualitative risk management
- Safran Risk
Safran Risk (formerly Pertmaster) delivers advanced risk analysis for project schedules and costs with emphasis on oil & gas, mining, and large infrastructure projects.
Key Features:
- Monte Carlo simulation with advanced statistical methods and correlation modeling
- Cost and schedule risk analysis integrated in single model
- Risk driver modeling linking uncertainties to multiple project activities
- Probabilistic forecasting with confidence intervals for completion and cost
- Sensitivity tornado diagrams and spider plots for risk prioritization
- Import/export with Primavera P6, MS Project, and Safran Planner
Best For: Mega-projects ($100M+), capital-intensive industries, organizations requiring sophisticated risk modeling, projects with significant technical uncertainty
Pricing Model: Subscription licensing approximately $3K-$5K per user annually
Pros: Most sophisticated risk analysis algorithms available, handles extremely large complex schedules, strong technical support, industry-proven methodology
Cons: Expensive, significant learning curve, requires statistical knowledge to use effectively, overkill for smaller projects, complex setup and configuration
Flexible/Mid-Market Solutions
- Risk Register by ProjectBalm
Risk Register provides streamlined cloud-based risk tracking focusing on ease of use and rapid deployment, ideal for teams new to formal risk management or managing moderate-complexity projects.
Key Features:
- Clean intuitive interface requiring minimal training
- Customizable risk register with probability/impact matrices
- Email notifications for risk assignments and updates
- File attachments and comment threads for collaboration
- Risk reporting with exportable charts and register exports to Excel
- Mobile-responsive web interface (no separate app required)
Best For: Small to mid-size project teams (5-50 people), organizations starting formal risk management, consulting firms managing multiple client projects, agile teams wanting lightweight risk tracking
Pricing Model: Subscription at $29-$49 per user monthly, depending on tier; 14-day free trial
Pros: Very easy to learn and deploy (hours, not weeks), affordable for small teams, no complex setup, responsive customer support, frequent updates
Cons: Limited advanced analytics, no Monte Carlo simulation, basic reporting, minimal integration capabilities, not suitable for enterprise-scale needs
- Tracker Suite
Tracker Suite offers configurable risk and issue management with strong workflow capabilities, suitable for organizations wanting flexibility to adapt tools to their processes.
Key Features:
- Unified risk, issue, action, and change management in single platform
- Highly configurable fields, workflows, and approval processes without coding
- Multiple risk assessment methodologies supported (qualitative and quantitative)
- Advanced filtering, sorting, and grouping for risk analysis
- Automated email notifications and escalations based on risk criteria
- Integration with MS Project, Jira, and ServiceNow via connectors
Best For: PMOs establishing standardized risk processes, organizations with unique workflow requirements, teams managing risks alongside issues and actions
Pricing Model: Subscription starting at $40 per user monthly; volume discounts for 25+ users
Pros: Excellent configurability, good value for functionality, responsive vendor, strong workflow engine, relatively quick implementation
Cons: Configuration requires some technical skill, reporting less visual than competitors, occasional performance issues with very large data sets, learning curve for advanced features
- Predict!
Predict! by Barbecana delivers schedule risk analysis specifically for Microsoft Project users, providing accessible quantitative risk analysis for project managers already using MS Project.
Key Features:
- Seamless Microsoft Project add-in (works within MS Project interface)
- Monte Carlo simulation for MS Project schedules
- Risk analysis showing the probability of meeting milestone dates
- Multiple simulation methods (PERT, custom distributions)
- Risk mitigation scenario comparison
- Simple licensing and deployment (install like any MS Project add-in)
Best For: MS Project users wanting to add risk analysis capability, project managers in IT, product development, events, and mid-market manufacturing
Pricing Model: Perpetual license, approximately $600 per user; annual support optional
Pros: Extremely affordable, minimal learning curve for MS Project users, no separate interface to learn, quick value demonstration, good documentation
Cons: MS Project dependency (no standalone capability), basic risk register features, limited collaboration, Windows-only, basic reporting
A Clear Comparison
| Software | Best For | Key Strength | Deployment | Price Range | Integration | Analytics Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Resolver | Enterprise GRC | Comprehensive compliance | Cloud/On-prem | $$$$$ ($50K-$200K/yr) | Extensive | Advanced |
| Fusion Framework | Portfolio/Program | Portfolio optimization | On-premise | $$$$ ($40K-$150K/yr) | Strong PPM | Advanced |
| LogicManager | Mid-Market ERM | User experience | Cloud | $$$-$$$$ ($25K-$100K/yr) | Good | Intermediate |
| Active Risk Manager | Schedule Risk | P6/MS Project integration | Desktop | $$$ ($1.2K-$6K/user) | Excellent PM tools | Advanced |
| RiskyProject | Schedule Analysis | Affordable quantitative | Desktop | $$ ($850-$1,800/license) | Good | Advanced |
| Safran Risk | Mega-Projects | Sophisticated modeling | Desktop/Cloud | $$$$ ($3K-$5K/user/yr) | Excellent P6 | Expert |
| Risk Register | Small Teams | Ease of use | Cloud | $ ($29-$49/user/mo) | Basic | Basic |
| Tracker Suite | PMO Processes | Configurability | Cloud | $$ ($40/user/mo) | Moderate | Intermediate |
| Predict! | MS Project Users | MS Project add-in | Desktop | $ ($600/license) | MS Project only | Intermediate |
Rating Scale:
- Price: $ = <$1K/user/yr, $$ = $1K-$5K, $$$ = $5K-$25K, $$$$ = $25K-$100K, $$$$$ = $100K+
- Integration: Basic = Import/Export, Moderate = API + few connectors, Good = Multiple connectors, Strong = Enterprise integrations, Excellent = Native deep integration, Extensive = Full GRC suite
- Analytics: Basic = Heat maps/matrices, Intermediate = Trend analysis, Advanced = Monte Carlo, Expert = Sophisticated statistical modeling
Software Selection Guide by Organization Size
Small Teams and Startups
Budget constraints typically limit options to sub-$5K annual investments. Small teams cannot justify $50K+ enterprise platforms when total project values are $500K-$2M. Every dollar spent on software competes with hiring, equipment, or marketing, ROI must be clear and immediate.
Simplicity requirements mean software must deliver value with minimal training investment. Teams of 5-15 people don’t have dedicated risk managers or full-time PMO staff. Tools requiring weeks of configuration, specialized administrators, or extensive training won’t get adopted—they’ll become expensive shelfware.
Recommended tools:
- Risk Register by ProjectBalm: $29- $49/user per month provides professional risk tracking without enterprise complexity. Quick setup, intuitive interface, and adequate reporting for investor or board presentations. Scales from single-project to small portfolio.
- Predict! for MS Project: A one-time $600 investment adds quantitative risk analysis if teams already use MS Project Professional. No ongoing subscription, minimal learning curve, sufficient for most small-project needs.
- Tracker Suite: At $40/user monthly, it provides good configurability for growing teams establishing risk processes they’ll scale later. Migration path to enterprise tools is easier than from spreadsheets.
Integration needs focus on affordable project management platforms (Asana, Monday.com, Smartsheet) and collaboration tools (Slack, MS Teams). Avoid solutions requiring enterprise infrastructure (on-premise servers, dedicated IT support) or expensive complementary systems (Primavera P6, SAP).
Mid-Size Organizations
Growing complexity characterizes the 50-500 employee segment, multiple concurrent projects, increasing stakeholder sophistication, emerging PMO functions, and pressure to demonstrate project governance maturity. Risk management transitions from “nice to have” to “business requirement.”
PMO establishment phase means organizations are standardizing methodologies, establishing governance frameworks, and implementing professional project management practices. Risk management software becomes part of broader PPM (Project Portfolio Management) initiatives. The selected tool should support standardization while providing sufficient flexibility for different project types.
Recommended tools:
- Active Risk Manager (ARM): $1.2K-$2K per user annually provides enterprise-grade schedule risk analysis at accessible price points. Strong for engineering, construction, manufacturing companies running $5M-$50M projects where schedule certainty matters. Excellent training resources support capability building.
- LogicManager: $25K-$60K annually (for 20-50 users) delivers modern cloud platform balancing enterprise features with user-friendly design. Good choice for service companies, healthcare, financial services where risk management spans operational and project domains.
- Tracker Suite: Affordable scalability, starts low, grows with team size. Strong configurability lets PMO tailor workflows without custom development. Good middle ground before jumping to six-figure enterprise platforms.
Scalability considerations are paramount. Software selected should accommodate 2-3x growth in projects and users over 3-5 years without requiring replacement. Cloud-based platforms offer better scalability than desktop tools with per-device licensing. Evaluate vendor roadmaps, upgrade paths, and migration complexity.
Enterprise and Complex Programs
Multiple projects/programs spanning business units, geographies, and functions create coordination complexity requiring portfolio-level risk visibility. CIOs need to understand aggregate technology risk, operations leaders need supply chain risk insight, and executives need strategic risk exposure across the enterprise.
Compliance requirements intensify in regulated industries, pharmaceuticals tracking validation risks, financial services managing operational risk for regulators, and aerospace documenting risk management for government contracts. Enterprise platforms provide audit trails, approval workflows, and documentation that satisfy regulatory scrutiny.
Recommended tools:
- Resolver: Industry-leading GRC platform for $50K-$200K+ provides integrated risk, compliance, audit, and incident management. Best fit for highly regulated enterprises (financial services, healthcare, energy) managing 50+ concurrent projects with complex governance.
- Fusion Framework System: $40K-$150K investment delivers sophisticated portfolio risk analytics. Ideal for capital project-intensive industries (infrastructure, oil & gas, mining, construction) where portfolio risk-adjusted prioritization drives billions in investment decisions.
- Safran Risk + Active Risk Manager: Combined deployment ($100K-$150K for 30-50 users) provides advanced quantitative analysis (Safran) with a broader adoption tool (ARM) for different user sophistication levels. Common in aerospace, defense, mega-infrastructure programs.
Enterprise integration needs encompass ERP (SAP, Oracle), PPM (Clarity, Planview), GRC platforms, business intelligence (Power BI, Tableau), and collaboration systems (SharePoint, Confluence). API-first architecture, pre-built connectors, and integration support become critical selection criteria. Budget 20-30% of software cost for integration development and maintenance.
| AVOID THIS MISTAKE
Selecting software based solely on feature checklists without evaluating user experience, adoption factors, and organizational readiness Why it’s problematic: The most feature-rich platform is worthless if nobody uses it. Many organizations buy sophisticated tools that require significant training, complex configuration, and ongoing administration, yet experience low adoption because the tools feel burdensome rather than helpful. Project managers revert to spreadsheets “just this once” and never return to the official system. What to do instead: Prioritize user adoption factors equally with features. Conduct user testing with actual PMs during evaluation (not just administrators). Assess training requirements realistically, if your PMs won’t attend 16 hours of training, don’t purchase tools that require it. Start with simpler, consistently used tools rather than sophisticated ones that languish unused. You can always upgrade later from a functioning simple system; you cannot salvage value from an unused complex system. |
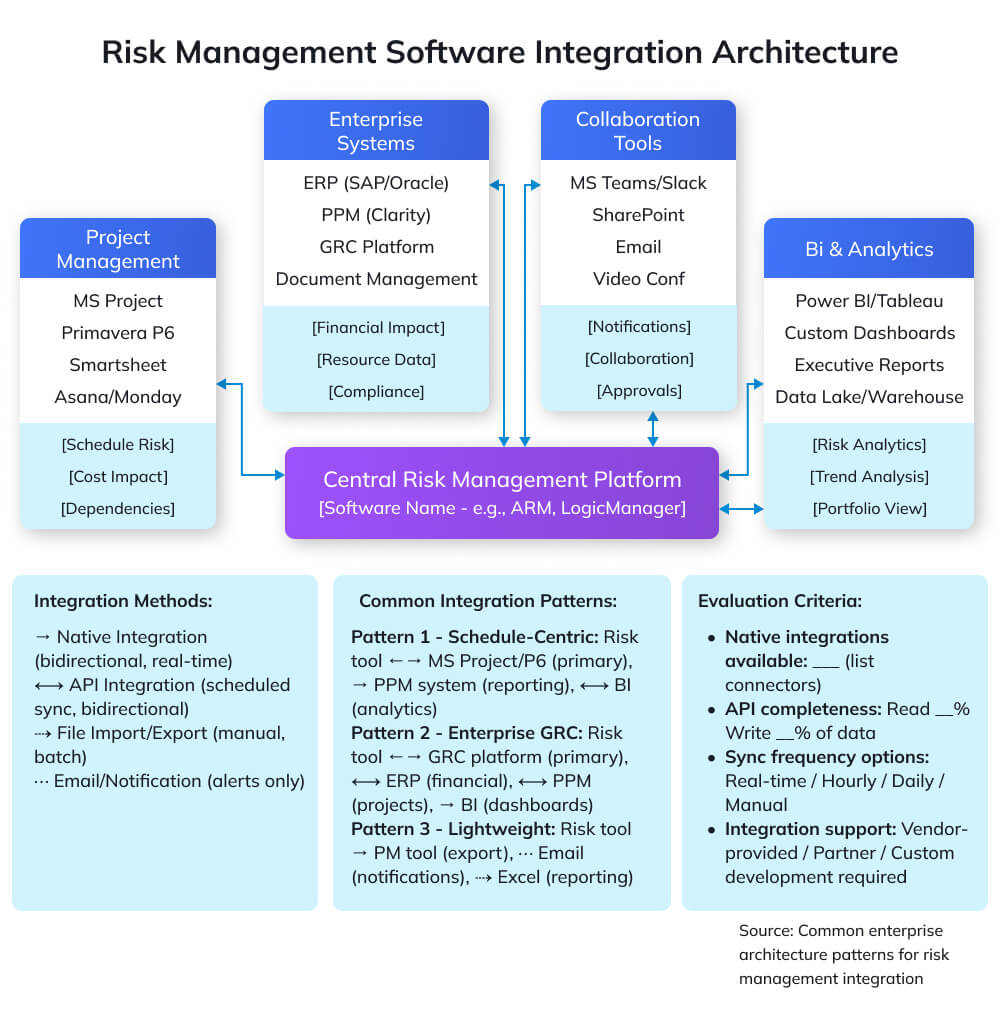
Integration Considerations
Project Management Tool Integration
MS Project, Primavera, and Smart sheet integration creates powerful synergy between risk management and schedule management. Two-way sync means: risks affecting specific schedule activities automatically update duration probability distributions, schedule delays trigger risk reassessment, and Monte Carlo simulations use actual project data rather than static assumptions.
Evaluate integration depth: Basic import/export requires manual steps and creates data staleness. API-based connectors enable scheduled synchronization (daily, hourly) maintaining reasonable currency. Native deep integration provides real-time bidirectional updates, the gold standard, but typically expensive and complex to maintain.
Two-way data sync importance cannot be overstated. One-way export from risk tools to PM tools helps but leaves risk data disconnected from project reality. When schedule changes don’t flow back to update risk probability, you’re managing risk based on outdated project assumptions, better than nothing, but far from optimal.
Enterprise System Integration
ERP, PPM, GRC platforms integration enables enterprise-wide visibility and consistent data. Risk exposure metrics flowing into PPM systems inform portfolio prioritization and investment decisions. Financial risk impacts syncing with ERP systems enable accurate forecasting and contingency management. Operational risks feeding GRC platforms ensure holistic enterprise risk perspective.
API capabilities determine integration feasibility. Modern REST APIs with comprehensive documentation enable custom integrations. Legacy systems with limited or proprietary APIs require expensive middleware or manual workarounds. Evaluate API completeness during selection, can you read and write all necessary data programmatically, or only export reports?
Reporting and BI Tools
Power BI, Tableau integration transforms risk data into executive insights. Pre-built connectors or ODBC/API access enable business intelligence analysts to combine risk data with financial performance, operational metrics, and strategic KPIs, revealing correlations between risk exposure and business outcomes.
Data export capabilities provide insurance against vendor lock-in and enable custom analytics. Ensure export formats include structured data (CSV, JSON, XML), not just formatted reports (PDF). A complete risk register export with all fields, history, and relationships preserves data when you switch platforms.
| PRO TIP: INTEGRATION EVALUATION
Test integrations with your actual data during trial periods, not just vendor demonstrations. Vendors showcase integrations using clean demo data with perfect field mapping and no edge cases. Real organizations have legacy data with inconsistent formats, custom fields not matching standard schemas, and unique workflows requiring special handling. Demand proof-of-concept integration using a subset of your actual project data, schedule files, and risk register before committing. Discover integration limitations during evaluation, not after six-figure purchase orders. |
Implementation Best Practices
Pilot Program Approach
Start small, scale gradually by selecting 1-3 pilot projects representing different project types, complexities, and stakeholder groups. Pilots allow learning without enterprise-wide disruption, generate success stories that build momentum, identify configuration needs before broad rollout, and provide ROI evidence justifying continued investment.
Selecting pilot projects strategically requires balance: Choose projects with engaged sponsors willing to invest time in new tools, but not your most critical projects where tool learning curves create unacceptable risk. Select projects with 6-12 month remaining duration providing sufficient time to demonstrate value before completion. Ensure diverse representation, include both technical and business projects, different organization units, and varying risk profiles.
Pilot duration typically runs 8-16 weeks, long enough to experience complete risk management cycles (identification, assessment, mitigation, monitoring, closure) but short enough to maintain momentum and reach go/no-go decisions before organizational priorities shift.
User Adoption Strategies
Training and change management determine success or failure more than software functionality. Comprehensive training programs should include: Role-based training (different depths for users vs. administrators vs. executives), hands-on workshops using actual organizational projects (not generic examples), quick reference guides and video tutorials for just-in-time learning, and regular refresher sessions as organizational memory fades.
Executive sponsorship provides the authority and visibility that drives adoption. Visible executive use, reviewing risk dashboards in leadership meetings, asking questions based on risk data, recognizing teams demonstrating excellent risk management, signals organizational importance. Without executive reinforcement, PMs view risk software as “extra work” rather than “how we do business.”
Create incentives and accountability: Include risk register completeness in project health scorecards, require risk analysis at project approval gates, and celebrate examples of early risk identification that prevented problems. Public recognition of teams that catch and mitigate significant risks reinforces desired behaviors.
Continuous Improvement
Regular reviews and optimization prevent risk management from becoming rote checkbox exercise. Quarterly reviews should assess Whether identified risks are the right risks or merely superficial compliance. Are mitigation strategies actually implemented, or documented and forgotten? Do risk assessments predict actual project challenges or miss real issues? Is the tool helping or hindering productivity?
Metrics tracking demonstrates value and identifies improvement opportunities: Number of risks identified per project (trending up suggests better identification), percentage of risks closed before impact (effectiveness metric), time from identification to documented mitigation plan (responsiveness), and correlation between risk exposure and project outcomes (validation that risk assessment predicts reality).
Refine risk categories, assessment criteria, and workflows based on lessons learned. Eliminate fields nobody uses, add fields repeatedly requested, adjust probability/impact scales if everything rates “medium,” and streamline workflows if approval delays undermine responsiveness.
| MASTER PROJECT RISK MANAGEMENT
PMI-RMP® Certification Training: Become a Risk Management Expert Software tools amplify your risk management capabilities, but expert knowledge drives value. Our PMI-RMP® certification training provides comprehensive coverage of global risk management frameworks, techniques, and best practices. What you’ll gain:
Who should enroll: Project managers, program managers, risk managers, PMO professionals seeking to master risk management at enterprise scale. |
Conclusion
Selecting risk management software is less about finding a “best” tool and more about finding the right fit for your context, team size, project complexity, regulatory environment, and technical maturity. Smaller teams may get the most value from simple, cloud-based risk registers that replace spreadsheets; mid-sized PMOs often need tools with workflow, reporting, and portfolio views; and large or highly regulated enterprises typically require full-fledged GRC platforms with deep analytics and integration.
Whatever you choose, success won’t come from features alone. Run a pilot, involve real users in the selection process, test integrations with your existing stack, and invest in training and adoption. Done well, the right tool turns risk management from reactive firefighting into proactive value protection, becoming a genuine competitive advantage for your projects and programs.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Do I need specialized risk management software if my PM tool has basic risk features?
It depends on your needs. Basic risk registers in tools like MS Project, Asana, or Smartsheet suffice for simple projects with 10–20 risks and qualitative assessment. However, they lack: quantitative analysis (Monte Carlo simulation), advanced visualization (dynamic heat maps), automated workflows, portfolio-level risk aggregation, and sophisticated reporting. If you manage complex projects, multiple concurrent initiatives, or face compliance requirements, dedicated tools provide substantial value beyond basic PM tool capabilities.
2. How long does a typical implementation take?
Implementation timelines vary dramatically by solution complexity: Simple cloud tools (Risk Register, Tracker Suite) deploy in days to 2–3 weeks with basic configuration. Mid-market solutions (Active Risk Manager, LogicManager) typically require 4-12 weeks including configuration, integration, training, and pilot testing. Enterprise platforms (Resolver, Fusion Framework) need 3–6 months for comprehensive deployment including customization, enterprise integration, change management, and phased rollout. Budget 2-3x vendor-estimated timelines for realistic planning.
3. Can we integrate risk management software with Jira or other agile tools?
Yes, though integration depth varies. Several risk tools offer Jira connectors or API integration enabling: risk identification from Jira issues, linking risks to specific epics/stories, and surfacing risk status in agile dashboards. LogicManager, Tracker Suite, and Resolver provide pre-built Jira integration. Others require custom API development. For agile environments, also consider whether the tool supports agile-friendly lightweight risk management versus heavyweight documentation processes that conflict with agile values.
4. What’s the difference between risk management software and GRC platforms?
Risk management software focuses specifically on project/program risk, identifying, assessing, and mitigating uncertainties affecting project objectives. GRC (Governance, Risk, Compliance) platforms address enterprise-wide risk including operational risk, strategic risk, compliance management, audit management, and policy governance across the organization. GRC platforms (Resolver, LogicManager) include project risk modules but emphasize broader enterprise risk management. Choose project-specific tools if you only need project risk management; choose GRC platforms if you need integrated enterprise-wide risk and compliance capabilities.
5. How do we convince executives to invest in risk management software?
Build business case emphasizing: Risk avoidance value (quantify historical project failures and cost overruns that better risk management could have prevented, even preventing one $500K overrun justifies significant software investment). Compliance and audit (if regulated, emphasize documentation, audit trails, and reduced audit findings). Portfolio optimization (demonstrate how risk-adjusted prioritization improves ROI across project portfolio). Competitive advantage (show how competitors use sophisticated risk management). Use pilot program to generate concrete ROI data before requesting enterprise-wide funding. Executive dashboards during trial showing portfolio risk exposure often create “aha moments” that secure investment.
6. Should we build custom risk management tools or buy commercial software?
Buy commercial software in 95% of cases. Custom development requires $100K-$500K+ investment plus ongoing maintenance, consumes internal IT resources needed for core business systems, creates vendor lock-in to internal developers, and delivers inferior results compared to vendors focused specifically on risk management. Custom development only makes sense for: extremely unique requirements no commercial tool addresses, situations where integration with proprietary legacy systems is mandatory, or when existing enterprise platform licensing (SharePoint, ServiceNow, Salesforce) makes customization cost-effective. For most organizations, configuring commercial tools delivers better results faster at lower total cost.
7. How do risk management tools handle cybersecurity and data privacy?
Reputable vendors implement: Encryption (data at rest and in transit using AES-256 and TLS), access controls (role-based permissions, multifactor authentication, SSO integration), audit logging (comprehensive tracking of data access and changes), compliance certifications (SOC 2 Type II, ISO 27001, GDPR compliance), and data residency options (specify geographic storage locations for regulatory compliance). During evaluation, request security documentation, penetration test results, and compliance certifications. For sensitive projects (defence, healthcare, financial), consider on-premises deployment or private cloud options to provide additional control. Avoid vendors that are unwilling to provide detailed security documentation or that have concerning security postures.