
PRINCE2 is a globally recognized methodology in project management that provides a structured and scalable approach to managing projects. Developed by the UK government, PRINCE2 offers a comprehensive framework that emphasizes controlled project execution, effective risk management, and clear communication channels. It has become a global standard for project management and is widely adopted across various industries and sectors.
Table of Contents
- What is PRINCE2?
- History and Evolution of PRINCE2
- Why is PRINCE2 Important?
- Elements of PRINCE2 Methodology
- Six Aspects of PRINCE2
- Various Roles Defined in PRINCE2
- What is PRINCE2 Project Management?
- PRINCE2 Methodologies vs. Alternative Methodologies
- Conclusion
In this blog post, we will explore the key components of PRINCE2, including its methodology, 7 principles, processes, and themes. Understanding these elements will give you valuable insights into how PRINCE2 can enhance project success and improve overall project management practices.
What is PRINCE2?
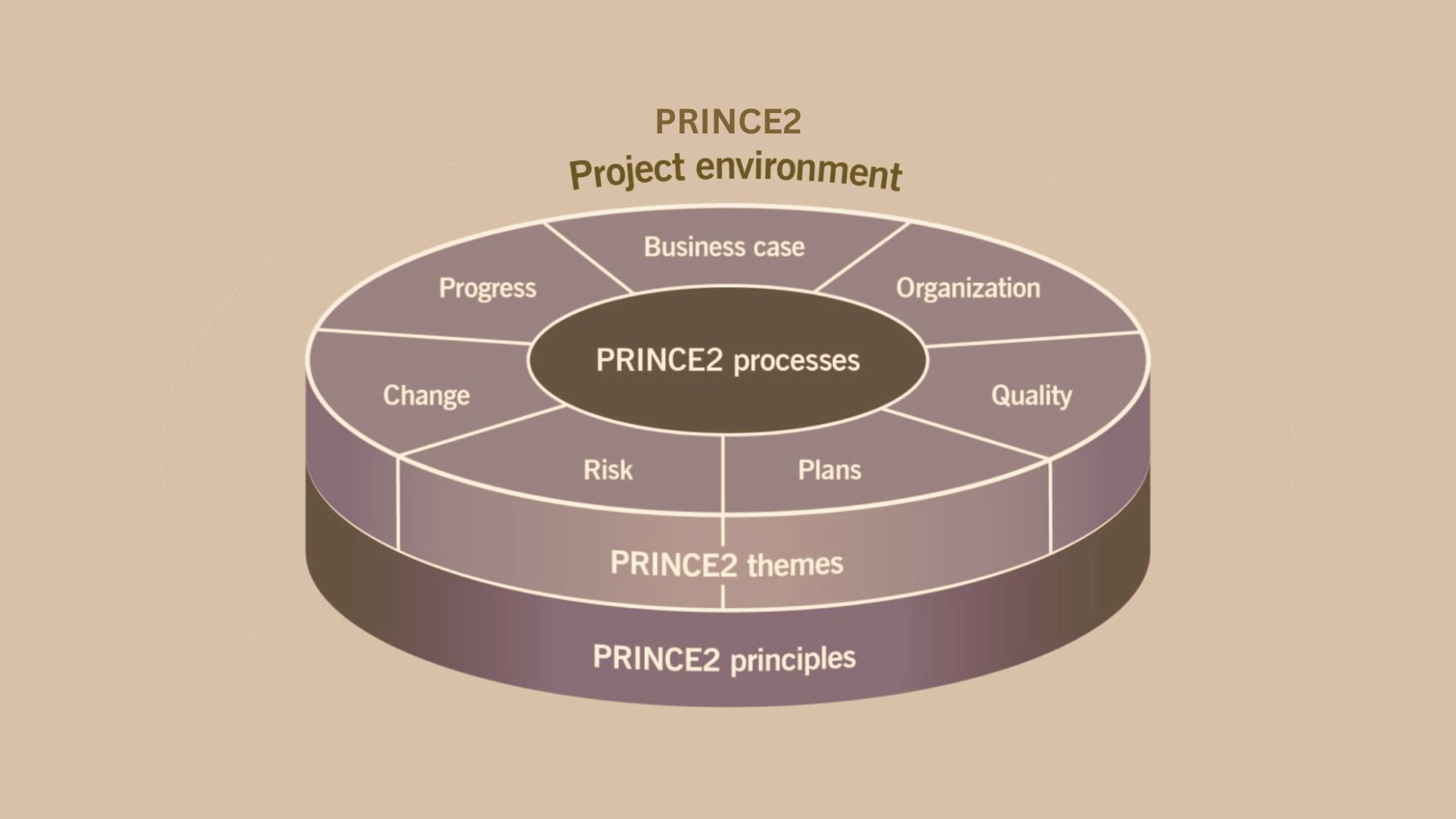
PRINCE2 (PRojects IN Controlled Environments) is a widely recognized project management methodology that provides a structured framework for managing projects of any size and complexity. Originating from the UK, PRINCE2 is used internationally and is known for its focus on organization, control, and quality. The methodology is built around seven principles, themes, and processes that guide the management and delivery of projects in a controlled environment.
PRINCE2 emphasizes clear roles and responsibilities, effective communication, and continuous evaluation and improvement, making it a versatile and reliable approach to project management. Its scalability and flexibility allow it to be tailored to the specific needs of different projects, ensuring consistent and successful outcomes.
History & Evolution of PRINCE2
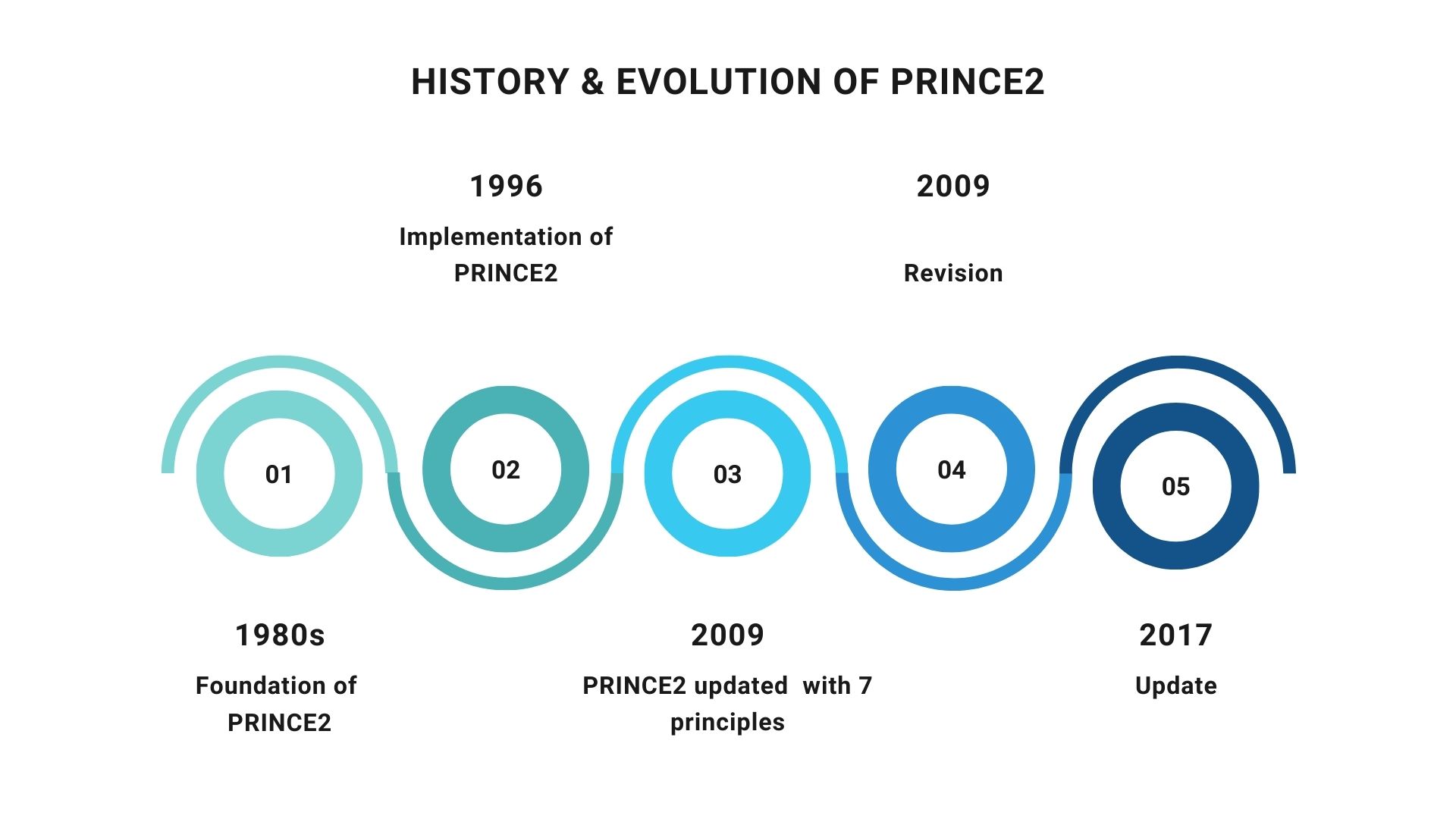
PRINCE2 has a long and interesting journey. It all started in the 1970s with a private sector framework called PROMPT, which aimed to tackle the problem of projects going over budget and schedule. The UK government then adopted a part of PROMPT in 1989, naming it PRINCE and using it for their IT projects.
However, PRINCE faced limitations. It was seen as too inflexible and not ideal for smaller projects. This led to the development of PRINCE2 in 1996. This evolved version addressed PRINCE’s defects by becoming more generic and adaptable. It could now be applied to various industries and project sizes. Since then, PRINCE2 has continued to be refined, with a focus on making it even more flexible and scalable.
Origins of PRINCE2
In 1989, the Computer and Telecommunications Agency (CCTA) was established. In April 1989, the CCTA renamed the framework from PROMPT II IN THE CCTA Environment to PRINCE and implemented it as an IT standard for project management. Civil Servants, therefore, chose to modify the framework’s name to the abbreviation PRINCE, which still stands for PRojects IN Controlled Environments. However, the framework was rarely used due to its rigidity and lack of adaptable characteristics for minor projects.
Evolution of PRINCE2
After several talks with project management experts and 150 European organizations, PRINCE2 was formed in 1996 as a best practice framework and an updated, more flexible framework than its predecessor. The PRINCE2 methodology significantly changed in 2009 when the seven core principles were developed. In 2013, ownership was transferred from HM Cabinet to AXELOS Ltd.
AXELOS has recently published the 2017 Update to PRINCE2. Beginning in 2017, it was decided that the PRINCE2 syllabus would be revised in response to feedback from world-renowned PRINCE2 Practitioners, who recommended a greater emphasis on the link between the themes and guidance and the application of the framework to real-world business scenarios. There are still the same ideas, procedures, and themes; however, the PRINCE2 tests and training techniques have been reorganized.
Recognition of PRINCE2 Globally
PRINCE2 has gained widespread recognition and acceptance worldwide, making it one of the most sought-after project management methodologies. Its global recognition stems from its comprehensive framework, adaptability to different industries, and alignment with international project management standards.
Numerous public and private organizations across various sectors have embraced PRINCE2 as their preferred approach to project management. Additionally, the availability of PRINCE2 certifications further solidifies its global recognition, as professionals worldwide seek to enhance their project management skills and validate their expertise in PRINCE2 methodology. The international recognition of PRINCE2 demonstrates its effectiveness in driving project success and establishing a common language and approach for project teams worldwide.
Why is PRINCE2 Important?
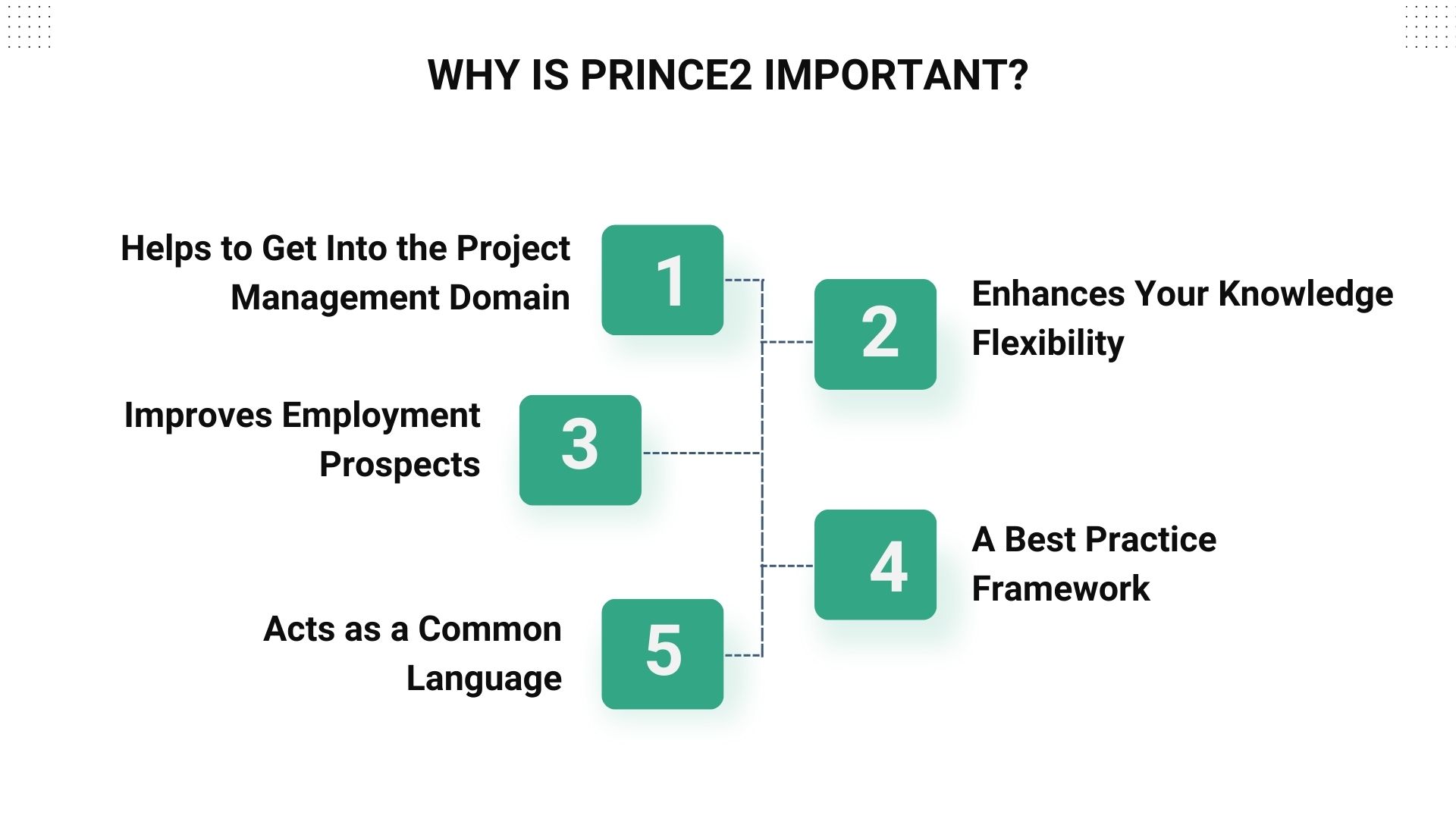
PRINCE2 benefits project managers, directors, and organizations by allowing for more control over resources and managing business and project risk more effectively. Therefore, it represents well-established and tested best practices in project management. We have listed a few of its advantages below.
1. Helps to Get Into the Project Management Domain
PRINCE2 is the industry standard for project management. It teaches you the skills you need to be confident in managing projects successfully. This is because PRINCE2 employs a common language, systems, and procedures. As a result, this gives you more control over your resources and risks.
2. Enhances Your Knowledge Flexibility
PRINCE2 is a best practice method customized to the specific needs of different organizations for all projects, including agile delivery. Hence, whatever your typical projects entail, PRINCE2 can handle them. In addition, you can gradually create a more customized and subjectively appropriate approach to project management for your organization by learning as you apply and tailor the framework.
3. Improves Employment Prospects
A PRINCE2 certification is an excellent addition to your resume. PRINCE2 is a world-class international product and the industry standard for project management. Over 1 million professionals worldwide are certified in PRINCE2, making it the most widely used project management methodology globally. So, it’s no surprise that many companies worldwide require PRINCE2 certification for their employees.
Looking for an option to improve efficiency of your project? Checkout this PRINCE2 Certification course now!
4. A Best Practice Framework
PRINCE2 is more than just a theory. The methodology is founded on practitioners’ expertise and practical knowledge from numerous industries and sectors. It also has a track record of success, with plenty of case studies to back up the efficacy of PRINCE2 best practices.
5. Acts as a Common Language
PRINCE2 fosters a smooth-running project environment by establishing a common language for all those involved. This means everyone from the project manager to team members and clients are on the same page. PRINCE2 achieves this through a shared set of terminology for key project concepts, ensuring everyone understands terms like “stage” and “deliverable” in the same way.
Elements of PRINCE2 Methodology
The PRINCE2 methodology comprises several essential elements that work together to provide a structured and controlled approach to project management. By integrating these elements, PRINCE2 enables organizations to establish a powerful foundation for successful project delivery, ensuring transparency, accountability, and adapting to evolving project requirements.
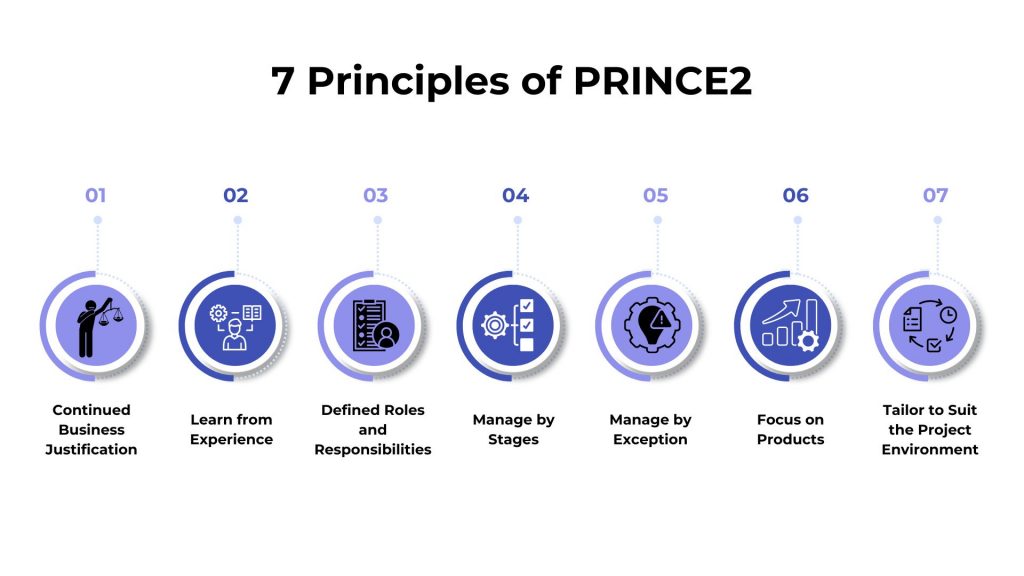
The 7 Principles of PRINCE2 are fundamental guidelines that form the core of the PRINCE2 methodology. These principles provide a framework for effective project management, ensuring that projects are managed consistently and successfully. Here are the 7 Principles of PRINCE2:
-
Continued Business Justification
Every project must have a valid business reason to justify its initiation and continuation. This principle ensures that resources are used only on projects that contribute to the organization’s objectives and deliver measurable benefits.
-
Learn from Experience
PRINCE2 emphasizes the importance of learning from previous experiences, both within the current project and from other projects. By capturing lessons learned and applying them to future projects, organizations can improve their project management processes and outcomes.
-
Defined Roles and Responsibilities
Clear roles and responsibilities are defined for each team member involved in the project. This principle ensures that everyone understands their duties and accountabilities, promoting effective decision-making and efficient project execution.
-
Manage by Stages
Projects are divided into manageable stages, each with its own defined objectives and deliverables. This staged approach allows for better control, monitoring, and flexibility in managing the project as it progresses.
-
Manage by Exception
PRINCE2 defines tolerance levels for each project objective to allow management by exception. This means that management intervention is only required when actual results deviate beyond acceptable tolerances, ensuring efficient use of management time and resources.
-
Focus on Products
PRINCE2 focuses on the definition and delivery of products (outputs) throughout the project lifecycle. By clearly defining product requirements and quality criteria, the methodology ensures that the final deliverables meet stakeholder expectations.
-
Tailor to Suit the Project Environment
PRINCE2 is scalable and can be tailored to suit the specific needs, size, complexity, and risks of the project. This principle emphasizes flexibility, allowing organizations to adapt PRINCE2 processes and practices to fit their unique project environments.
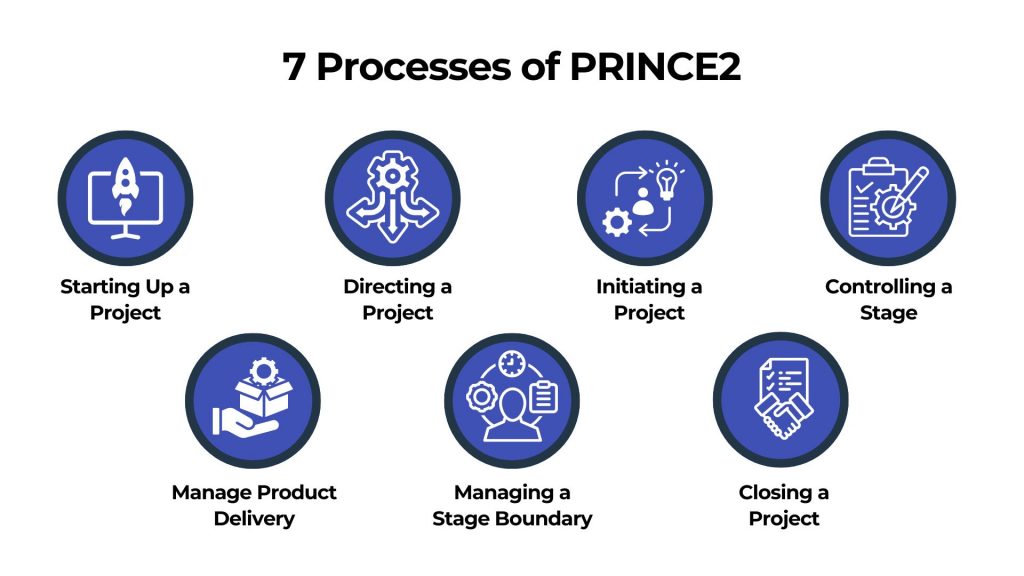
7 Processes of PRINCE2
PRINCE2 processes describe the evolution from the pre-project activity of getting started throughout the project life-cycle until the end of the project. Each process has agendas of suggested activities, products, and related duties. The project manager supervises the seven techniques and confirms them with the task board. Here is a breakdown of each stage.
PRINCE2 processes describe the evolution from the pre-project activity of getting started throughout the project management lifecycle until the end of the project.
Each process has agendas of suggested activities, products, and related duties. The processes describe a progression from the pre-project activity of getting started to the project lifecycle stages and the final act of project closure. Therefore, each process includes a suggested activities, products, and responsibilities checklist. Following are the procedures of PRINCE2:
-
Starting Up a Project
The starting up of a project process initiates the project by defining its scope, objectives, and approach. Key activities include appointing the project manager, identifying stakeholders, and preparing the project brief. This phase ensures that there is a clear understanding of why the project is needed and establishes a solid foundation for further planning.
-
Directing a Project
Directing a project provides overall governance and decision-making authority. It involves activities such as setting up the project board, defining responsibilities, and approving project initiation and stage plans. The project board monitors progress, manages risks, and ensures alignment with organizational objectives throughout the project lifecycle.
-
Initiating a Project
Initiating a project focuses on detailed planning and preparation. It includes defining the project scope, objectives, timelines, and resources. This process establishes project controls, such as change control procedures and communication channels. By the end of this phase, the project team and stakeholders have a clear understanding of what will be delivered and how it will be achieved.
-
Controlling a Stage
Controlling a stage manages the day-to-day activities within each project stage. It involves monitoring progress against stage plans, managing risks and issues, and ensuring that products (deliverables) are produced according to quality standards. This process ensures that each stage stays within agreed tolerances and delivers the expected outcomes.
-
Manage Product Delivery
Managing product delivery oversees the creation and delivery of project products (outputs). It focuses on coordinating activities to ensure that products are produced according to agreed specifications and timelines. This process involves assigning work packages to team members, monitoring progress, and reporting on product status to the project manager.
-
Managing a Stage Boundary
Managing stage boundaries marks the end of one stage and the beginning of the next. It involves reviewing completed work against the stage plan, updating the project plan as necessary, and preparing for the next stage. This process includes obtaining approval from the project board to proceed and ensuring that all deliverables meet quality criteria before moving forward.
-
Closing a Project
Closing a project finalizes all project activities and formally ends the project. It includes reviewing project achievements against the initial business case, capturing lessons learned, and handing project deliverables to the operational team or client. This process ensures that all loose ends are tied up, resources are released, and stakeholders are satisfied with the project outcomes.
7 Themes of PRINCE2
The 7 themes of PRINCE2 are essential elements that must be addressed continuously throughout the project. They provide guidance on various aspects of project management, ensuring that the project remains controlled, organized, and aligned with its objectives. Here are the 7 themes of PRINCE2 explained in detail:
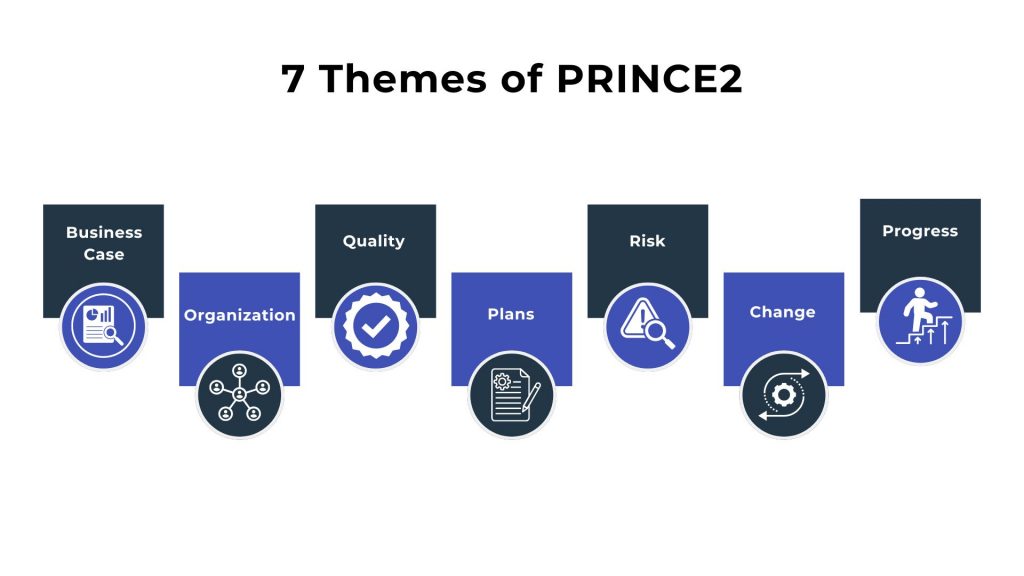
Business Case
The business case theme ensures the project remains desirable, viable, and achievable throughout its lifecycle. It involves developing a business case document that justifies the investment in the project and is reviewed and updated at key points to ensure the project continues to provide value to the organization.
Organization
The organization theme defines the project’s structure of accountability and responsibilities. It identifies the project management team and outlines roles such as the project board, project manager, and team members. This theme ensures everyone understands their roles and responsibilities, promoting clear governance and effective decision-making.
Quality
The quality theme ensures that the project’s deliverables meet the agreed-upon quality standards. It involves defining quality criteria, planning how to achieve these standards, and implementing quality control measures. This theme ensures that the outputs are fit for purpose and meet stakeholder expectations.
Plans
The plans theme outlines how to develop and maintain project plans. It covers the steps required to create plans at various levels (e.g., project, stage, and team plans), ensuring that plans are realistic and consistent and provide a basis for monitoring and controlling the project’s progress.
Risk
The risk theme deals with identifying, assessing, and controlling risks and opportunities that may impact the project. It involves creating a risk management strategy and maintaining a risk register to track and manage potential threats and opportunities. This theme ensures that proactive measures are taken to mitigate risks and exploit opportunities.
Change
The Change theme focuses on managing changes to the project baseline, which includes the project’s scope, deliverables, and plans. It involves setting up a change control process to evaluate and approve changes, ensuring that only beneficial and necessary changes are implemented. This theme helps maintain control over the project’s direction and outcomes.
Progress
The Progress theme monitors and controls the project’s progress against the planned objectives. It includes setting up mechanisms for tracking performance, reporting progress, and managing deviations from the plan. This theme ensures that the project stays on track and that any issues or delays are addressed promptly.
Six Aspects of PRINCE2
The PRINCE2 methodology identifies six aspects that each project must manage. First, project managers must utilize KPIs to evaluate performance objectives and project constraints. Following are the six aspects of PRINCE2:
| Category | Description |
| Scope | What labor is necessary to complete the project? The project plan should include an explanation of the project’s scope |
| Costs | What is the cost of your project? The project costs are also specified in the project plan |
| Timescales | How much time will it take to finish your project? The project plan describes each phase of the project and its duration |
| Risk | What are the risks to your project? You’ll need a risk management strategy to determine the mitigation strategies employed |
| Quality | What quality requirements do your customers or stakeholders have? To meet quality standards, you must have quality control and assurance procedures |
| Benefits | Every project requires a business case and a cost-benefit analysis to articulate its objective and financial or strategic benefits |
Various Roles Defined in PRINCE2
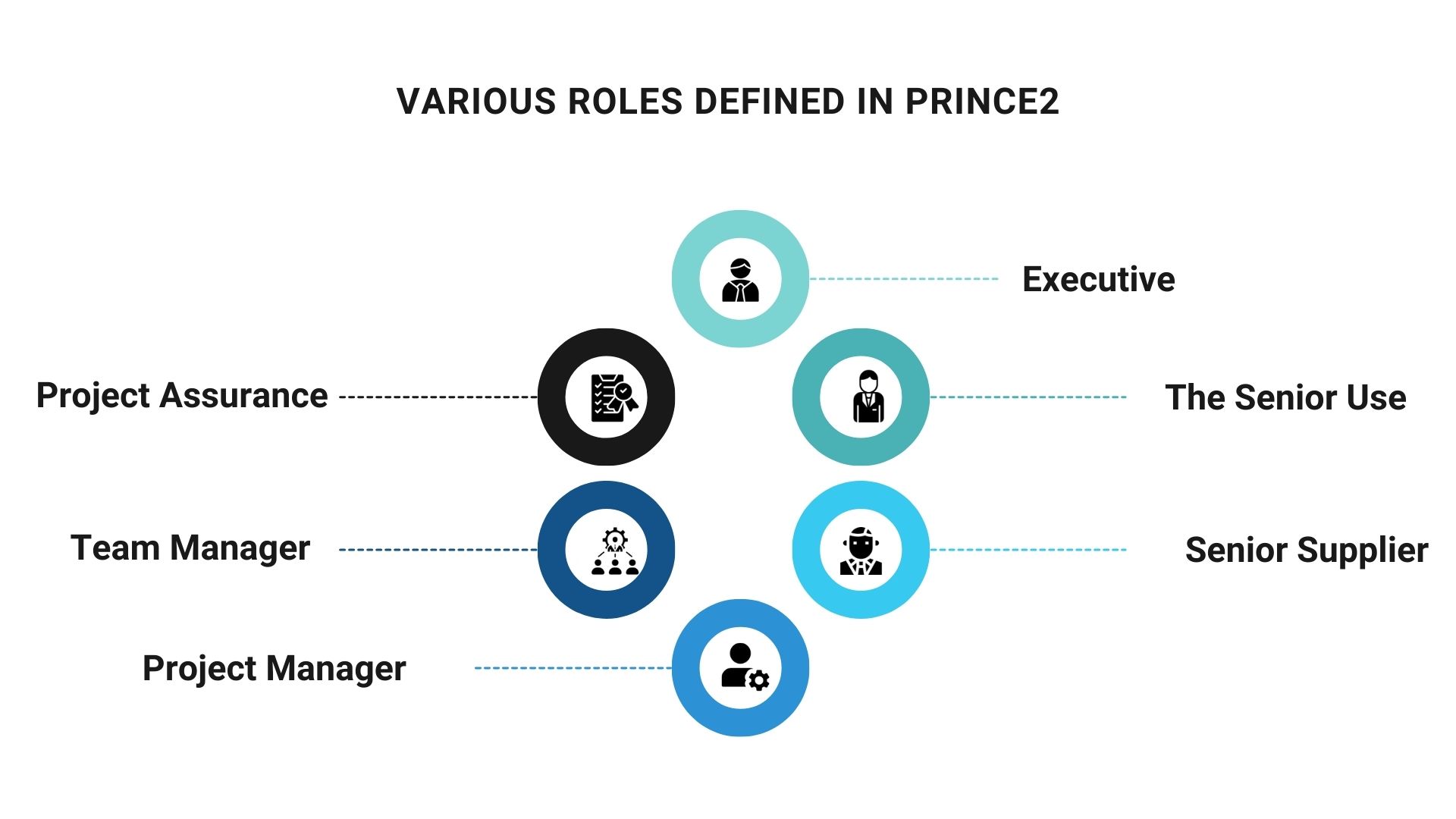
PRINCE2 is one of the most widely used project management methodologies today. It is based on the concept of project roles. Therefore, the method specifies nine filled roles, even if the same person fills multiple roles. The following are the roles under the PRINCE2 methodology:
Executive
The executive secures project funding and maintains the project’s business case and justification. However, they accept the project’s deliverables and focus on the project’s benefits to the organization or the program or portfolio that the project is a part of, similar to a “project sponsor” in other methodologies. So, the executive appoints the project board and project management team.
The Senior Use
This represents the organization or people who will use the PRINCE2 project’s product or service. Those who will be affected by it directly. The customer and the user may be the same. In addition, the senior user ensures that the Project Board respects the user’s needs and that these are specified in the project.
Senior Supplier
The suppliers are all individuals and organizations who carry out the project work, i.e., those who create the project’s deliverables. It consists of internal (the project team) and external (suppliers). It may also include those who will support and maintain the products after the completion of the project.
Firstly, the senior supplier represents the suppliers’ interests. Secondly, suppliers typically want to be fairly compensated for their efforts and receive a positive reference for future work. In addition, work satisfaction ranks high on the list as well.
Project Manager
The project manager oversees the project’s planning, execution, controlling, and closure phases. So, project managers form a project team and keep track of its progress. In addition, they make a project plan that includes a timeline and a budget and communicate with the project team and customers.
Team Manager
The Team Manager is a lower-level manager in charge of the project’s deliverables daily. They are responsible to the project manager. They may have a large project team supporting them or do all of the work themselves, but they are the technical experts.
The team manager creates work packages, which are then assigned to project team members for completion. A series of work packages is transformed into a management stage.
Project Assurance
At predetermined intervals, Project Assurance provides an independent assessment of project progress. The Project Board commonly fills this role, which must be independent of the Project Manager. The Project Board may, however, appoint an independent project assurance team. Moreover, this team is responsible for keeping the project on track with business assurance, user assurance, and supplier assurance.
What is PRINCE2 Project Management
PRINCE2 plays a crucial role in project management by effectively providing a structured and standardized approach to managing projects of varying scales and complexities. With its emphasis on clear governance, risk management, and stakeholder engagement, PRINCE2 enables project managers to maintain control, mitigate risks, and deliver projects within defined timeframes and budgets.
By implementing PRINCE2 principles, processes, and themes, organizations can enhance project success rates, improve communication and collaboration among project teams, and ensure alignment with business objectives. PRINCE2’s systematic approach empowers project managers to navigate challenges, make informed decisions, and achieve desired project outcomes, making it a valuable methodology in project management.
PRINCE2 Methodology vs. Alternative Methodologies

As a project manager, you devote most of your attention to selecting your team’s appropriate project management approach. A methodology often provides a framework consisting of procedures, practices, principles, and aspirations to direct the progress of a project. PRINCE2 has demonstrated its effectiveness and is now a well-known project management method. Considering the above mentioned considerations, you may determine if PRINCE2 is suitable for their projects and teams.
If you believe this is not the appropriate framework, numerous more prevalent alternatives exist. The following are popular project management methodologies:
- Agile project Management Methodology
- Scrum Methodology
- Kanban Methodology
- Lean Methods
It is up to the project manager to choose an approach. The best way to make this decision is by analyzing the project’s needs, the available resources, and the project team’s capacity to adhere to the methodology.
Conclusion
PRINCE2 is a highly regarded project management methodology providing a structured and scalable framework. With its focus on controlled project execution, effective risk management, and clear communication channels, PRINCE2 has become a global standard in project management.
By understanding the methodology, principles, processes, and themes of PRINCE2, professionals can enhance their project management skills, improve project success rates, and effectively align projects with organizational objectives. Whether new to PRINCE2 or looking to expand your knowledge, embracing this methodology can lead to more efficient project delivery, increased stakeholder satisfaction, and overall project success.
With its proven track record and wide adoption across industries, PRINCE2 offers a robust and adaptable approach to project management that can drive positive outcomes and propel organizations toward success in their project endeavors.













