Have you ever wondered about the scalability of agile methodologies as a business expands? The Spotify model in Agile is an example of a successful transition. This model has enabled Spotify to reach new heights while maintaining the benefits of agile, which is often reserved for smaller teams and businesses.
It is the world’s largest and most popular audio streaming subscription service, with an estimated 286 million users. As we delve into the intricacies of this model, inspired by the renowned music-streaming platform, we aim to provide a comprehensive understanding for agile practitioners, project managers, and organizational leaders seeking to optimize collaboration and efficiency.
This blog offers valuable insights into how the Spotify Model has influenced team dynamics and project management certification courses across diverse industries.
Table of Contents:
- What is the Spotify Model?
- Key Elements of the Spotify Model
- The Benefits of the Spotify Model
- Challenges in Implementing the Spotify Model
- Best Practices of Using the Spotify Model
- Examples of Companies That Have Used the Spotify Model
- Conclusion
What is the Spotify Model?
The Spotify Model is an organizational framework for Agile software development that was popularized by Spotify but has since been adopted and adapted by many other organizations. It is not a strict, one-size-fits-all model but rather a set of agile practices and principles that aim to foster innovation, collaboration, and adaptability within large and growing organizations.
The model is known for its unique approach to organizing teams, emphasizing autonomy, and promoting a culture of continuous improvement.
Spotify Model emphasizes decentralized, cross-functional teams known as “squads,” organized into larger units called “tribes.” The model encourages autonomy, collaboration, and a culture of continuous improvement.
Squads focus on specific features, while tribes unite squads with shared missions. The model also incorporates “chapters” and “guilds” for organizing expertise and knowledge sharing.
The Spotify Model is often associated with a culture of experimentation and learning, encouraging teams to adapt their processes to suit their context best. It has gained attention for its ability to scale Agile practices in a way that aligns with the dynamic and fast-paced nature of the tech industry.
Key Elements of the Spotify Model
At the core of the Spotify model is a focus on simplicity. When Spotify initially devised its organizational structure, it pinpointed a few crucial components that outlined the structure of individuals and teams.
The Spotify Model provides an Agile organizational framework that balances autonomy and alignment within a large and growing organization. The model is designed to enhance collaboration, innovation, and adaptability. Here are key elements of how the Spotify Model works:
-
Squads
Squads are small, cross-functional teams consisting of developers, designers, and other necessary roles (6-12 members). Each squad is responsible for a specific aspect of product development. They operate autonomously, managing their tasks, priorities, and schedules.
They embody the Agile principle of a self-organizing, empowered team. The purpose of squads is to streamline the development process, enhance communication, and increase efficiency by breaking down the work into manageable units.
-
Tribes
Tribes are collections of squads ((3-5 Squads) that share a common mission or goal. These squads work together to achieve larger objectives aligned with the organization’s strategy. They provide a higher organizational structure, fostering collaboration among related squads.
The coordination among squads within a tribe ensures alignment with the broader mission. Tribes facilitate the scalability of Agile practices and encourage a sense of unity among teams with shared objectives.
-
Chapters
Chapters are groups of individuals with similar skills or expertise, regardless of their squad affiliation. For example, all front-end developers across different squads may belong to the same chapter. They offer a platform for knowledge sharing, mentorship, and skill development. Members of a chapter collaborate on best practices and advancements within their domain.
Chapters enhance expertise and professional development, ensuring that individuals with similar skills can share knowledge and stay updated on industry trends.
-
Guilds
Guilds are informal communities that cut across squads and chapters, focusing on specific areas of interest or expertise. Guilds facilitate collaboration and learning beyond the boundaries of squads or chapters.
It allows individuals to connect, share ideas, and collaborate on topics of common interest. They serve as a means for cross-pollination of ideas and best practices. Guilds promote a culture of continuous learning, innovation, and knowledge sharing across the organization.
-
Trio
The Trio, or TPD Trio, is a combination of a Tribe Lead, Product Lead, and Design Lead. Each tribe has a Trio to ensure continuous alignment between these three viewpoints when working on feature areas. It collaborates to guide and align the tribe’s efforts.
It ensures a balanced representation of leadership, product vision, and design considerations in decision-making. The Trio enhances coordination and collaboration within a tribe, ensuring that strategic and design perspectives align with the overall mission.
-
Alliance
Alliances are combinations of Tribe Trios (typically three or more) that work together to achieve a common goal that transcends the scope of individual tribes. It provides a framework for multiple tribes to collaborate on significant projects or organizational objectives. They promote collective efforts toward larger goals.
Alliances facilitate cooperation and coordination between tribes, enabling them to work together on initiatives that require a unified effort.
The Benefits of the Spotify Model
The Spotify Model, an Agile organizational framework, offers several benefits that contribute to its popularity and adoption among various industries. Here are the key advantages of the Spotify Model:
- Agile Scalability: The model is designed to scale Agile practices effectively, making it suitable for both small teams and large, complex organizations. Its modular structure, including Squads, Tribes, Chapters, and Guilds, facilitates adaptability and growth
- Cross-Functional Collaboration: By organizing teams into Squads that consist of members with diverse skills, the model promotes cross-functional collaboration
- Autonomy and Ownership: Squads operate with a high degree of autonomy, allowing team members to make decisions independently. This autonomy fosters a sense of ownership and accountability, empowering teams to deliver high-quality results
- Clear Mission Alignment: Tribes unite multiple Squads under a common mission or goal. This alignment ensures that teams work toward shared objectives, promoting a unified organizational vision
- Reduced Bureaucracy: The Spotify Model minimizes hierarchical layers, reducing bureaucracy and decision-making bottlenecks. This streamlined approach allows for faster response to changes in the market or business priorities
- Innovation and Creativity: The model’s flexibility and encouragement of experimentation contribute to an environment conducive to innovation and creativity. Teams are empowered to explore innovative ideas and approaches, driving continuous innovation
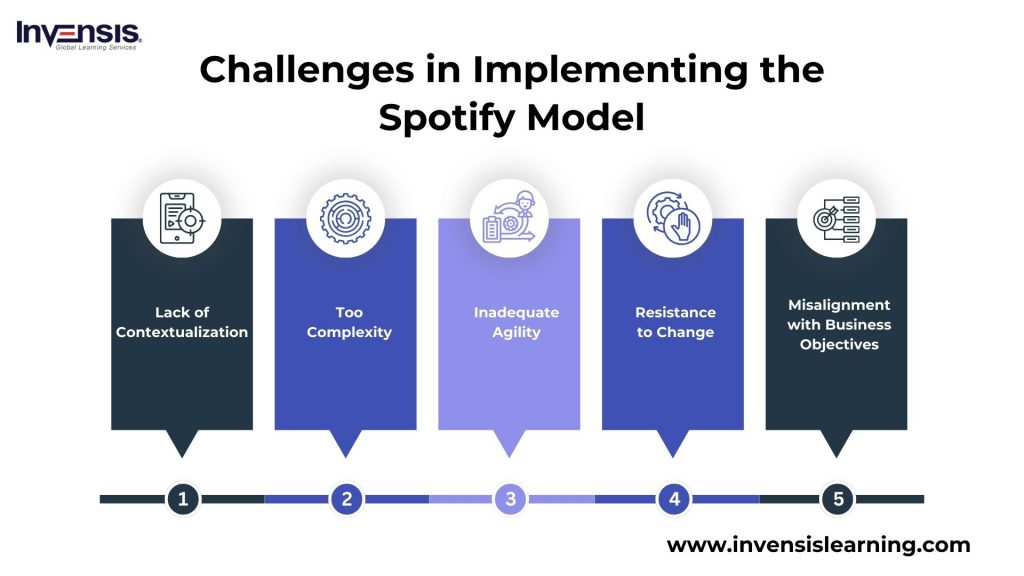
Challenges in Implementing the Spotify Model
The Agile at Scale model, also known as the Spotify model, was introduced by Spotify to tackle the challenges associated with extending Agile practices beyond a few teams. Despite its widespread adoption and initial success, the model has encountered criticism and instances of failure. Here are several challenges contributing to implementing the Spotify Model:
-
Lack of Contextualization
The Spotify model, designed for Spotify’s specific culture and objectives, faced challenges when applied by other organizations without proper contextualization. This lack of adaptation led to confusion, inefficiencies, and failure.
It’s essential to recognize that every organization has unique needs, goals, and structures. While the Spotify model can be inspirational, blindly copying it is not advisable. Organizations should focus on adapting the model to their own context for successful implementation.
-
Too Complex
The Spotify model constitutes a sophisticated framework comprising numerous teams, tribes, chapters, and guilds, demanding considerable coordination, collaboration, and communication. This complexity may pose challenges, particularly for smaller organizations or those with less experienced teams.
While it can benefit larger organizations with well-established Agile practices, it might overwhelm and confuse others. Thus, organizations should diligently evaluate their maturity level, complexity, and specific needs before opting for the adoption of the Spotify model.
-
Inadequate Agility
Contrary to its name, the Spotify model has faced criticism for not aligning closely with Agile principles. Critics argue that the model’s perceived rigidity, bureaucracy, and hierarchy deviate from the core tenets of Agile. Organizations should strive to balance structure and flexibility, processes and people, to ensure alignment with Agile principles.
-
Resistance to Change
Adopting the Spotify model requires a significant shift in organizational culture, structure, and mindset, which can pose challenges. Resistance from teams and individuals may lead to a lack of buy-in and engagement.
Achieving this transformation goes beyond framework adoption; it demands a deep understanding of the organization’s culture, values, and strong leadership. Therefore, organizations should invest in change management, training, and coaching for a smoother transition to the Spotify model.
-
Misalignment with Business Objectives
While the primary emphasis of the Spotify model is on enhancing the efficiency and effectiveness of software development and delivery, it may not seamlessly synchronize with broader business goals and objectives.
This misalignment can result in a lack of strategic impact. Organizations should take measures to align their Agile practices with the overarching business strategy, ensuring the delivery of value to both customers and stakeholders.
Best Practices of Using the Spotify Model
Implementing the Spotify Model involves adhering to best practices that optimize its benefits and align with Agile principles. Here are key best practices for using the Spotify Model:
-
Avoid Replication of the Model
Instead of blindly copying the Spotify Model, organizations should focus on adapting it to their unique context. Tailor the model to align with your organization’s culture, structure, and specific needs.
Every organization is distinct, and a one-size-fits-all approach may not be effective. Customization ensures that the model is well-suited to address a particular organization’s specific challenges and requirements.
-
Emphasize Autonomy and Trust
Foster an environment that values autonomy and trust within teams. Provide teams with the authority to make decisions independently, encouraging a sense of ownership and accountability.
Autonomy empowers teams to innovate, make swift decisions, and take ownership of their work. Trust is essential for building a collaborative and high-performing organizational culture.
-
Maintain Transparency Within the Community
Prioritize open and transparent communication within the organization. Ensure that information flows freely among teams, squads, and individuals, promoting a shared understanding of goals and progress.
Transparency fosters a culture of openness, reduces ambiguity, and enhances collaboration. It enables everyone to be well-informed and aligned with organizational objectives.
-
Promote a Culture that Encourages Mistakes
Create a culture that views mistakes as opportunities for learning and improvement. Encourage teams to experiment, take risks, and see failures as valuable lessons. A culture that accepts mistakes promotes innovation and resilience. It allows individuals to stretch their boundaries, learn from experiences, and continuously iterate on processes for better outcomes.
Examples of Businesses Implementing the Spotify Model
While the Spotify Model has been influential in the tech industry, it’s important to note that not all aspects of the model may be publicly disclosed by organizations. However, some companies have openly shared their experiences implementing agile practices inspired by the Spotify Model. Here is an example of the Spotify model implementation of Zalando:
Zalando, a European e-commerce company specializing in fashion, has been recognized for implementing agile practices inspired by the Spotify Model. While not a replica, Zalando has adopted a structure that includes elements such as tribes, squads, and chapters, reflecting the principles of the Spotify Model.
Here’s a breakdown of how Zalando has implemented agile practices:
- Tribes: Zalando organizes its teams into tribes, which are groups of squads aligned around common missions or goals. This allows for a more holistic and collaborative approach to achieving larger organizational objectives
- Squads: Squads within Zalando are small, cross-functional teams responsible for specific product features or components. These squads operate with high autonomy, managing their tasks and making decisions independently
- Chapters: Similar to the Spotify Model, Zalando has chapters, which are groups of individuals with similar skills or expertise. These chapters provide a platform for knowledge sharing, skill development, and mentorship within specific domains
- Agile Practices: Zalando’s adoption of agile practices extends beyond the organizational structure. The company emphasizes agile principles such as continuous improvement, regular retrospectives, and a focus on collaboration and flexibility
Zalando aims to enhance its responsiveness, efficiency, and collaboration in the rapidly evolving e-commerce landscape by implementing agile practices inspired by the Spotify Model. Adopting such practices reflects a commitment to fostering a culture of innovation and adaptability within the organization.
Conclusion
We hope this article provided insights into the Spotify model, its operational dynamics, and potential challenges when integrating it into your business framework. Initially employed by Spotify during its tech startup phase, the model has become widely recognized for its streamlined approach to scaling agile operations, serving as a blueprint for various tech firms.
However, it’s important to note that Spotify has moved away from this model, emphasizing the absence of a universally perfect management style. Before implementing the Spotify Agile Model, it’s crucial to consider your organization’s context, as goals, workflows, and work culture may differ significantly.
A copy-and-paste approach from other businesses is discouraged, as identical outcomes cannot be guaranteed.
Elevate your project management skills with Invensis Learning’s Agile certification Courses. Gain expertise in Agile methodologies and lead successful projects with confidence. Enroll now for comprehensive training and propel your career to new heights.