Embarking on the Agile journey involves embracing adaptability and continuous learning.
At its core is the Agile retrospective—a powerful practice change improvement within teams.
So, what exactly is it?
It is actually a dedicated time or a session for reflection at the end of each iteration, where teams assess successes, identify improvements, and enhance processes.
This blog explains Agile retrospectives, exploring concepts and methodologies for sustainable improvement.
Whether you’re experienced or new to Agile, you will be able to discover actionable insights and real-world examples to enable transformative growth.
Table of Contents:
- What is an Agile Retrospective?
- Importance of Agile Retrospectives
- Points of Discussion Between Teams in Agile Retrospective Meetings
- Format of Agile Retrospective
- Ideas and Tips to Conduct Agile Retrospectives
- Types of Agile Retrospective Techniques
- Conclusion
What is an Agile Retrospective?
An Agile retrospective is a structured and collaborative meeting that occurs at the end of an iteration or project in Agile development. Its primary purpose is to facilitate a team’s reflection on the recently completed work, encouraging open communication and constructive feedback.
During the retrospective, team members collectively assess what went well and what could be improved and identify actionable items for enhancing future processes. This reflective practice is a foundation of Agile methodologies, enabling a culture of continuous improvement by empowering teams to adapt, iterate, and optimize their workflow for increased efficiency and success in subsequent iterations.
Importance of Agile Retrospectives
Agile retrospectives are crucial as they have the capability to facilitate ongoing enhancements, support teamwork, and adjust to the changing demands of a project.
Here are key aspects that highlight the significance of Agile retrospectives:
Continuous Improvement: Agile retrospectives provide a dedicated space for teams to reflect on their processes and outcomes, fostering a culture of continuous improvement. By identifying what worked well and what could be enhanced, teams can iteratively refine their approaches.
Enhanced Team Collaboration: Retrospectives create a safe space for open communication and collaboration. Team members can share their perspectives, insights, and feedback, creating a stronger sense of shared responsibility and collaboration.
Adaptability to Change: Through regular retrospectives, teams become more adaptable. They can assess and adjust their strategies based on the lessons learned from previous iterations, ensuring they remain responsive to changing project dynamics.
Problem Identification and Resolution: Retrospectives help teams identify and address challenges early. This approach minimizes issues, leading to smoother execution and better outcomes.
Increased Productivity: Implementing improvements identified during retrospectives leads to increased productivity over time. Teams refine their practices based on retrospective insights, contributing to sustained high performance.
Goal Alignment: Retrospectives help ensure that team efforts align with project goals. This alignment is crucial for maintaining focus, direction, and a shared understanding of how individual contributions contribute to overall project success.
Points of Discussion Between Teams in Agile Retrospective Meetings
In Agile retrospective meetings, teams engage in focused discussions to evaluate their performance and collaboratively identify areas for improvement.
Here are the points during these meetings:
- Successes and Achievements: Celebrate successes and achievements from the iteration. Acknowledge what went well and analyze the contributing factors to replicate positive outcomes
- Challenges and Obstacles: Identify challenges and obstacles faced during the iteration. Discuss the core causes and explore potential solutions to overcome these limitations in future iterations
- Process Efficiency: Evaluate the efficiency of the team’s processes. Discuss whether the established workflows were effective, and explore opportunities for streamlining or optimizing processes.
- Communication: Discuss the effectiveness of communication within the team. Identify any communication breakdowns, misunderstandings, or information gaps and explore ways to enhance communication channels.
- Collaboration: Assess the level of collaboration among team members. Discuss instances of successful collaboration and identify areas where collaboration could be strengthened for improved teamwork.
- Customer Feedback: Discuss any feedback received from customers or stakeholders. Analyze the feedback and explore ways to incorporate valuable insights into future iterations.
- Team Morale: Assess team members’ overall morale and satisfaction. Discuss any factors that may have positively or negatively impacted morale and explore ways to maintain a positive team culture.
- Tools and Resources: Evaluate the effectiveness of tools and resources used during the iteration. Discuss whether the team had the necessary resources and if there are any improvements needed in the tools or infrastructure.
These points of discussion contribute to a comprehensive retrospective analysis, promoting a culture of continuous improvement and collaboration within Agile teams.
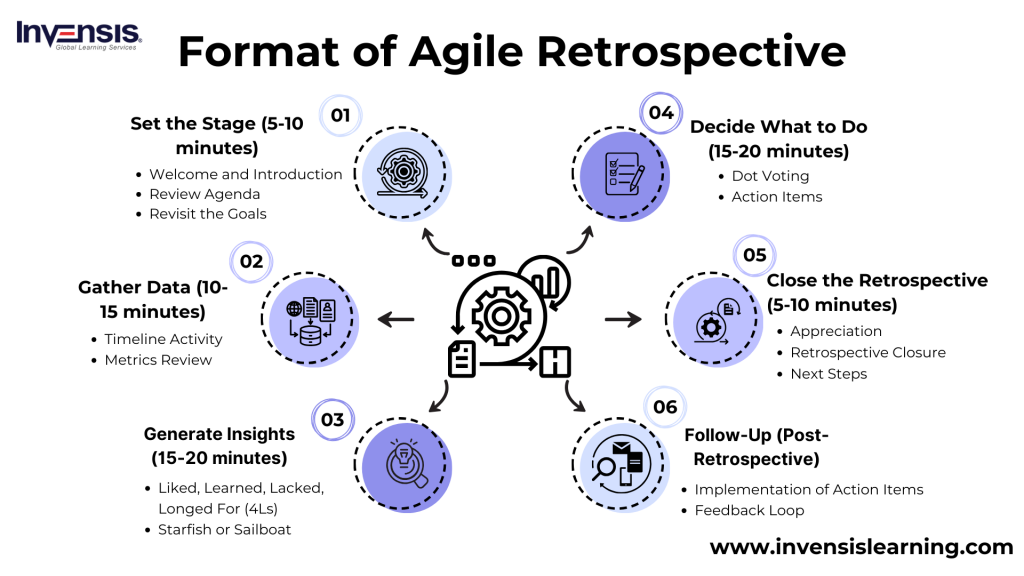
Format of Agile Retrospective
The format of an Agile retrospective typically follows a structured agenda to ensure a focused and productive discussion.
Here’s a common format for an Agile retrospective meeting:
Set the Stage (5-10 minutes)
- Welcome and Introduction: Start with a brief welcome to the team and introduce the retrospective purpose
- Review Agenda: Outline the agenda for the retrospective, ensuring everyone understands the flow of the meeting
- Revisit the Goals: Remind the team of the overarching goals of the retrospective—continuous improvement and team collaboration
Gather Data (10-15 minutes)
- Timeline Activity: Create a visual timeline of the iteration, marking key events, milestones, and feelings. This can serve as a reference point for discussions
- Metrics Review: Analyze relevant metrics or performance data from the iteration. This may include velocity, burn-down charts, or other project-specific metrics
Generate Insights (15-20 minutes)
- Liked, Learned, Lacked, Longed For (4Ls): Have team members share their perspectives on what they liked, learned, lacked, and longed for during the iteration
- Starfish or Sailboat: Use visual tools like the Starfish or Sailboat diagrams to prompt discussions on what should be continued, added, improved, reduced, or eliminated
Decide What to Do (15-20 minutes)
- Dot Voting: Prioritize the most important topics or improvement ideas by allowing team members to vote with dots on a board
- Action Items: Based on discussions and voting, collaboratively decide on specific action items for improvement. Assign responsibility and set a timeline for implementation
Close the Retrospective (5-10 minutes)
- Appreciation: Let team members appreciate each other’s contributions during the iteration
- Retrospective Closure: Summarize key takeaways, action items, and commitments made during the retrospective
- Next Steps: Discuss any immediate next steps or preparations for the upcoming iteration
Follow-Up (Post-Retrospective)
- Implementation of Action Items: Ensure the agreed-upon action items are implemented in the next iteration
- Feedback Loop: Establish a feedback loop to assess the impact of the changes and gather insights for future retrospectives
This format provides a structured framework for Agile teams to conduct retrospectives, promoting a balance between reflection, data-driven analysis, and actionable outcomes. Teams may also experiment with various retrospective formats or activities to keep the process engaging and effective over time.
Ideas and Tips to Conduct Agile Retrospectives
Conducting effective Agile retrospectives requires thoughtful planning and execution. Here are some ideas and tips to enhance the success of your Agile retrospective meetings.
-
Rotate Facilitators
Encourage team members to take turns facilitating retrospectives. This promotes shared ownership and diversity in perspectives and becomes exhausted in any one individual.
-
Vary Retrospective Formats
Keep retrospectives engaging by experimenting with different formats. Utilize techniques like Start-Stop-Continue, 4Ls, or visual aids such as charts and diagrams to stimulate discussion and insights.
-
Include Remote Team Members
If your team is distributed, leverage technology to include remote members in the retrospective. It is recommended to use video conferencing and online collaboration tools to maintain inclusivity.
-
Timebox Activities
Set time limits for each phase to maintain focus and efficiency. Timeboxing encourages concise discussions and ensures that retrospectives are brief.
-
Create a Safe Environment
Cultivate an environment of openness and safety, ensuring that team members feel at ease sharing their thoughts and offering constructive feedback. Emphasize that retrospectives are engaged towards improvement, steering away from a culture of blame.
-
Focus on Actionable Items
Ensure that discussions produce concrete, actionable outcomes. Identify precise measures the team can implement to overcome challenges and leverage opportunities in the upcoming iteration.
-
Regularly Schedule Retrospectives
Maintain a consistent schedule for retrospectives at the end of each iteration. Regularity fosters a continuous improvement mindset and provides a structured framework for reflection.
-
Emphasize Solutions
When discussing challenges, shift the focus to identifying solutions. Encourage a proactive mindset within the team, promoting problem-solving and constructive actions for improvement.
By incorporating these eight points, Agile teams can establish a foundation for effective retrospectives that contribute to continuous improvement, collaboration, and a positive team culture.
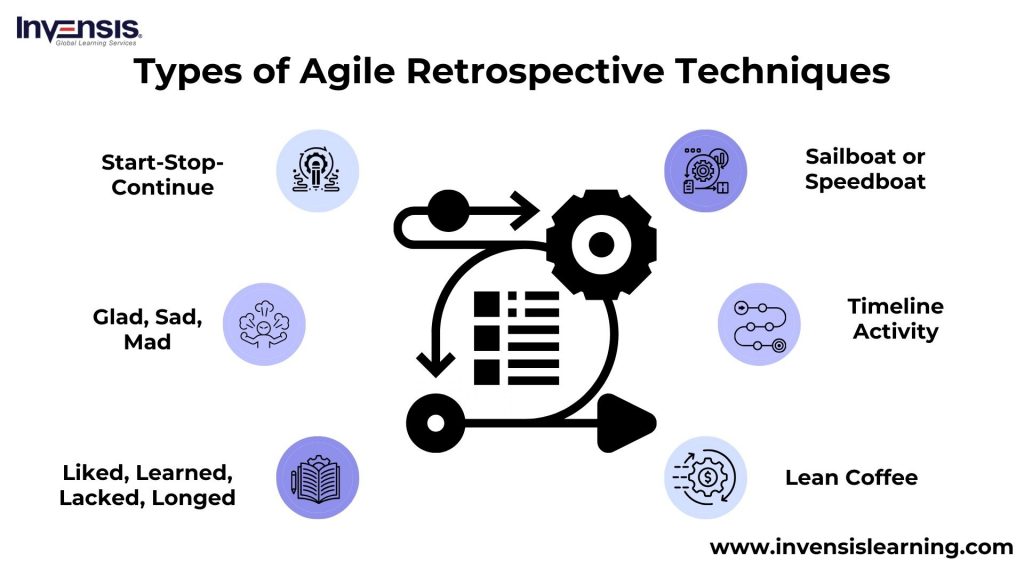
Types of Agile Retrospective Techniques
Agile retrospectives benefit from various techniques designed to stimulate meaningful discussions and insights. Here are several types of Agile retrospective techniques commonly used by teams.
-
Start-Stop-Continue
Teams reflect on activities to start, stop, or continue. This straightforward approach prompts actionable insights and helps in refining team practices.
-
Glad, Sad, Mad
Participants express what made them glad, sad, or mad, providing valuable insights into emotional responses and uncovering positive and negative aspects.
-
4Ls (Liked, Learned, Lacked, Longed For)
Teams categorize feedback into what they liked, learned, lacked, and longed for. This structured approach ensures a comprehensive exploration of team experiences.
-
Sailboat or Speedboat
Team members visually represent positive factors (winds) and obstacles (anchors) using a sailboat metaphor. This technique offers a clear visualization of progress and impediments.
-
Timeline Activity
Teams create a visual timeline of events, milestones, and feelings during the iteration. This provides a powerful reference for discussions and helps identify patterns over time.
-
Lean Coffee
In this dynamic, participant-driven format, team members suggest topics, vote on the agenda, and engage in time-boxed discussions. It promotes collaborative decision-making and adaptability.
These selected techniques offer a mix of simplicity, creativity, and structured analysis, catering to various team preferences and ensuring a holistic approach to retrospectives.
Conclusion
The Agile retrospective stands as a cornerstone in the continuous improvement journey for Agile teams. This ultimate guide has delved into the core principles, methodologies, and best practices that define this transformative ritual.
By dedicating time at the end of each iteration to reflect on achievements, challenges, and opportunities, teams can foster a culture of collaboration, adaptability, and innovation.
The significance of the Agile retrospective lies in its ability to propel teams towards greater efficiency and success by empowering them to fine-tune their strategies. As we conclude this exploration, remember that embracing the Agile retrospective is not just a practice but a commitment to a mindset that prioritizes learning, adaptability, and the relentless pursuit of excellence in every iteration.
Elevate your Agile project management proficiency with the Invensis Learning Agile Project Management Certification Courses, ensuring your team is aligned with industry best practices for successful project delivery.