An Assistant Project Manager role could be your perfect starting point. In this blog, we’ll delve into what it means to be an Assistant Project Manager, exploring the key responsibilities, skills required, and the pathway to stepping into this dynamic role. This position is a crucial stepping stone for those aiming to become full-fledged Project Managers, offering hands-on experience and industry insight.
Table of Contents:
- What is an Assistant Project Manager?
- What Does an Assistant Project Manager Do?
- What are the Skills Required to Become an Assistant Project Manger?
- How to Become an Assistant Project Manager?
- Salary of an Assistant Project Manager
- Conclusion
What is an Assistant Project Manager?
An Assistant Project Manager(APM) plays a key role in successfully executing organizational projects. This position demands a proactive approach to overseeing various aspects of a project, aligning closely with the directives of a project manager.
The responsibilities are diverse and include overseeing project goals, generating and presenting detailed reports, and analyzing data derived from project execution. These tasks require a keen eye for detail, an analytical mindset, and the ability to communicate effectively across different levels of the project team.
To step into this role, individuals often need a solid foundation of experience, typically garnered through years of service in related positions. Becoming an assistant project manager often starts with foundational organizational roles, progressively moving up the ladder through demonstrated capability and leadership skills.
The success of an assistant project manager lies in their leadership and communication skills. These skills are essential for guiding teams, ensuring project goals are met efficiently, and the smooth execution of project plans. This role demands technical proficiency and a strong ability to manage people and processes effectively.
For those aspiring to climb the career ladder in project management, starting as an Assistant Project Manager offers a valuable opportunity to hone these skills and gain the necessary experience to advance into higher project management roles.
What Does an Assistant Project Manager Do?
The role of an assistant project manager encompasses a range of responsibilities that are critical to the successful execution of projects. Their duties are multifaceted, often requiring a balance of technical know-how and strong interpersonal skills.
Here’s a comprehensive overview of what an assistant project manager typically does:
- Project Coordination and Support: APMs are key in coordinating project activities ensuring tasks are completed on time and within budget. This involves working closely with project teams, stakeholders, and suppliers.
- Communication and Reporting: Effective communication is a cornerstone of this role. Assistant project managers must communicate clearly and continuously with project teams and stakeholders. They prepare and deliver detailed project reports, updating on progress, challenges, and milestones.
- Data Analysis and Problem-Solving: Analyzing project data to assess performance and identify areas for improvement is another crucial aspect. They use these insights to troubleshoot problems and propose solutions.
- Resource Management: Managing resources effectively, whether human resources, materials, or time, is vital. They ensure that resources are allocated efficiently and are used to achieve optimal results.
- Quality Control: Ensuring that project outputs meet the required standards and expectations. This involves regular monitoring and evaluation of project deliverables.
- Risk Management: Identifying potential risks and developing mitigation strategies is essential for project success. They are working on foreseeing possible issues that could derail the project and planning accordingly.
- Assisting with Project Planning: While the primary planning is often the project manager’s responsibility, the assistant project manager contributes significantly to this process, providing input based on their understanding of project dynamics.
- Meeting Facilitation: APMs often organize and facilitate project meetings, ensuring that discussions are productive and that action items are clearly defined and followed up on.
The role of an assistant project manager is dynamic, requiring a blend of technical skills, project management knowledge, and soft skills like leadership and communication. This position serves as a critical support system for the project manager and the project team, contributing significantly to the project’s overall success.
Assistant Project Manager: Key Responsibilities and Duties
In the role of an assistant project manager, several core responsibilities and duties are critical to the position. This part of the job description is essential, as it outlines the regular functions the assistant project manager will perform. It also details how the position integrates within the organization and specifies the reporting manager.
Key responsibilities include:
- Engaging with clients to understand their project goals, ensuring clear and consistent communication regarding project specifics
- Working alongside the project manager to generate client invoices based on the services provided. This involves calculating costs involving labor, materials, equipment, and other expenses
- Creating detailed written estimates for clients, considering costs like labor, materials, and additional expenses
- Regularly visit project sites to monitor progress and address customer concerns or queries
- Liaise with site managers to discuss project delays or other issues and communicate these effectively to clients
- Developing digital Operation and Maintenance (O&M) manuals for project documentation
- Scanning and archiving important project documents like digital blueprints and schematics for future reference and access
These responsibilities underscore the multifaceted nature of the assistant project manager’s role, highlighting their importance in ensuring project success and client satisfaction.
What are the Skills Required to Become an Assistant Project Manger?
To excel as an assistant project manager, certain skills are essential. These skills not only facilitate effective management of projects but also ensure smooth coordination among teams and stakeholders.
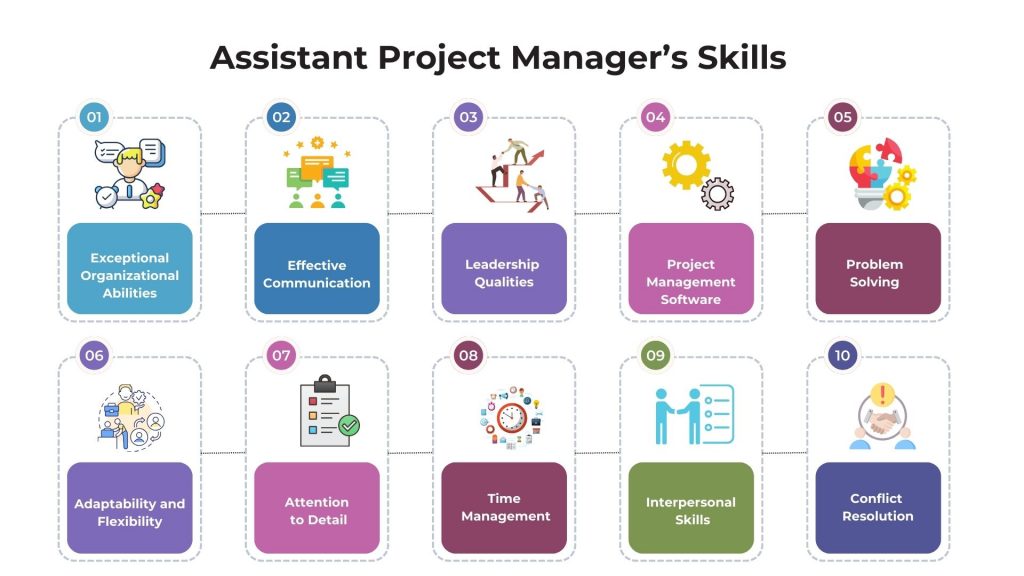
Here are some of the key skills required:
- Exceptional Organizational Abilities: Given that an assistant project manager often juggles multiple projects simultaneously, top-notch organizational skills are crucial. This involves adeptly managing budgets, schedules, and plans.
- Effective Communication: The ability to convey information clearly and succinctly is vital, especially since assistant project managers frequently liaise with diverse teams and departments. This skill is also crucial for successful interactions with vendors and suppliers.
- Leadership Qualities: Strong leadership skills are essential for motivating teams and driving projects toward completion. Effective leadership involves delegating tasks appropriately and inspiring team members.
- Proficiency in PM Software: Familiarity with relevant management software (like Microsoft Suite or industry-specific tools) is critical. This technical know-how aids in efficient project management and data handling.
Additional skills that significantly benefit Assistant Project Managers include:
- Problem-Solving and Critical Thinking: The ability to analyze situations, identify potential issues, and devise effective solutions is key to managing projects successfully.
- Adaptability and Flexibility: Projects often face unforeseen changes or challenges. Being adaptable and flexible enables an assistant project manager to navigate these changes effectively.
- Attention to Detail: Paying close attention to all aspects of a project ensures that nothing is overlooked and that the project’s quality is maintained.
- Time Management: Efficiently managing one’s time and the project’s timeline is essential to meet deadlines and keep the project on track.
- Interpersonal Skills: Building and maintaining strong relationships with team members, stakeholders, and clients is crucial for collaborative and successful project execution.
- Conflict Resolution: The ability to address and resolve conflicts that may arise within the team or with external parties is important to maintain a harmonious and productive work environment.
These skills form the backbone of an effective assistant project manager, enabling them to manage projects efficiently and lead teams effectively. Continuous development and honing of these skills are essential for career growth and success in this role.
Invensis Learning offers top Project Mangemnent courses align with industry requirements! Enroll Now!
How to Become an Assistant Project Manager?
Becoming an assistant project manager involves education, experience, skill development, and obtaining relevant certifications.
Here’s a comprehensive guide on how to embark on this career path:
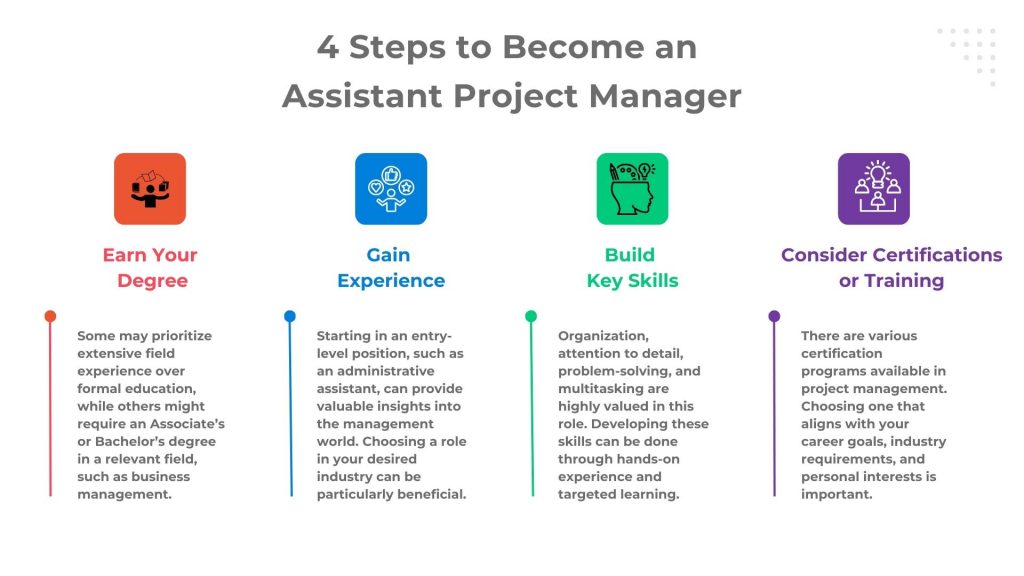
-
Earn Your Degree
- Education Requirement: The educational background required varies across companies. Some may prioritize extensive field experience over formal education, while others might require an Associate’s or Bachelor’s degree in a relevant field, such as business management.
- Relevance of Major: While a degree in project management is advantageous, majors in related fields like architecture, construction management, or engineering can also provide a solid foundation, especially for industry-specific project management roles.
- Training and Certifications: Acquiring professional certifications in project management can significantly boost your resume. These certifications demonstrate expertise and commitment beyond what a college degree can provide.
2. Gain Experience
- Entry-Level Positions: Starting in an entry-level position, such as an administrative assistant, can provide valuable insights into the management world. Choosing a role in your desired industry can be particularly beneficial.
- Internships: Internships offer a practical understanding of the assistant project manager’s role. They also provide opportunities to observe and learn from experienced project managers.
3. Build Key Skills
- Interpersonal Skills: Communication and interaction with team members, vendors, and stakeholders are crucial.
- Essential Skills: Organization, attention to detail, problem-solving, and multitasking are highly valued in this role. Developing these skills can be done through hands-on experience and targeted learning.
4. Consider Certifications or Training
- Certification Options: There are various certification programs available in project management. Choosing one that aligns with your career goals, industry requirements, and personal interests is important. Certificates like CAPM Exam Prep and Project Management Fundamentals Certification will help them become APMs.
- Research and Selection: When selecting a certification or training program, consider factors like industry relevance, time commitment, and financial investment. Invensis Learning is one of the best choices for this.
By combining formal education, practical experience, skill development, and professional certifications, you can effectively prepare for a successful career as an assistant project manager. Each step in this process contributes to building a strong foundation in project management principles and practices.
Salary of an Assistant Project Manager
Various factors, including location, industry, education, experience, and certifications, influence the salary of an assistant project manager. Understanding these elements can help you gauge potential earnings and make informed career decisions.
1. Location
- Geographical Impact: Salary levels for assistant project managers can vary significantly based on location. States like Washington, Nevada, and New Hampshire offer higher salaries, while Florida, Oklahoma, and Mississippi are among the lower-paying states.
- Regional Variations: These disparities are often due to the cost of living, demand for skills, and the economic climate in different regions.
2. Industry
- Sector Influence: The industry APM works in is critical in determining your salary. The highest-paying sectors include Telecommunications, Construction, Information Technology, Energy, Mining, Utilities, and Government/Public Administration.
- Industry-Specific Demand: Salary levels can reflect the demand for project management skills within these industries and the complexity of projects handled.
3. Education and Experience
- Educational Background: Most companies require at least a Bachelor’s degree, often in business management or a related field. Specialized programs in project management can also be advantageous.
- Work Experience: Prior experience in project management teams or administrative roles can enhance your capabilities and potentially lead to higher salaries. Experience in your chosen industry can also be beneficial, providing specific insights and skills relevant to that sector.
4. Certification
- Professional Certifications: Obtaining project management certifications can significantly boost your career prospects. These certifications demonstrate advanced skills in scheduling, budgeting, and reporting.
- Impact on Earnings: Certifications such as the PMI Project Management Professional (PMP) are recognized globally and can lead to higher earning potential. They signal employers a commitment to the field and higher expertise.
An Assistant Project Manager’s salary is not fixed and can vary widely. Considering these factors is important when evaluating job opportunities and career paths. Continuous professional development through education and certification can lead to better job prospects and higher salaries.
Conclusion
Embarking on a career as an Assistant Project Manager offers a dynamic and rewarding path, rich with opportunities for growth and development. This role is crucial in project management, requiring a blend of technical skills, leadership abilities, and a strong commitment to continuous learning. From understanding the key responsibilities and skills needed to the steps involved in becoming an assistant project manager and the factors influencing salary, this guide provides a comprehensive overview for those aspiring to this position.